西藏土壤可蚀性 κ 值驱动因素与空间分布预测

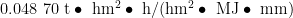
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:X53 文献标识码:A文章编号:1673-9868(2025)10-0120-14
DOI:10.13718/j.cnki.xdzk.2025.10.011
Prediction of Driving Factors and Spatial Distribution of Soil Erodibility K Value in Xizang
CHEN Songyan1,2, WANG Yongxia1, LIU Zhongyuan1,2, LI Chao¹², CHEN Qinyin1,², YU Wu1,2
1.ColegeofForestryandGrasslandSiences,XizangAgriculturalandAnimalHusbandryUniversityLinzhiXizang86ooChina;
2.Alpine Soil and Water Conservation Research Center,Xizang Agricultural and Animal Husbandry University, Linzhi Xizang 860000,China
Abstract : The K value of soil erodibility is a key indicator for predicting soil erosion and evaluating the effectiveness of soil and water conservation measures. Based on the second soil census data and field sampling data of Xizang,combined with environmental covariates,this paper uses big data to estimate the regional soil erodibility K value. The results showed that: ① Three models can be used to predict the spatial variability of K values:Ordinary Kriging(OK),Random Forest (RF)and Polygon Connection (PC). Among them,the RF model had more accurate prediction results compared to the PC and OK models,and its R2 was 0.781. The Root Mean Square Eror(RMSE),Mean Absolute Error(MAE) and Mean Relative Error(MRE) were 0.004,O.003 and O.00l,respectively. ② The importance results showed that the importance of topography, climate and vegetation to the prediction of K value was 35.04% , 31.31% and 29.88% ,respectively. The importance of human activities in the prediction of K value was only 3.77% : ③ The estimated value of K ranges from 0.016 05 to .Areas with high and medium-high erosion,medium and medium-low erosion and relatively low and low erosion account for 24.73% , 44.61% and 30.66% of the total area of Tibet,respectively. ④ The spatial uncertainty of RF prediction shows that the uncertainty is relatively high in the central,western,and northern regions,and relatively low in the eastern and southern regions,with the uncertainty index generally ranging from O. 271 to 0.816.
Key words: soil erodibility K value;driving factors;mapping model;spatial distribution characteristics
土壤侵蚀是自然界普遍存在的现象,也是我国面临的重大生态安全问题。(剩余14798字)