酸化改良对紫色水稻土羟基自由基生成的影响

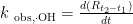
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:X53;S155. 2+92 文献标识码:A文章编号:1673-9868(2025)10-0110-10
DOI: 10.13718/j.cnki. xdzk. 2025.10.010
Abstract: This study investigated the efects of different soil amendments on the apparent yield and generation pathways of hydroxyl radicals (⋅OH ) in acidified purple paddy soil. The results showed that the application of soil amendments increased the soil pH and soil organic matter (SOM) content. Different amendments also had varying effects on the apparent production of ·OH in acidified purple paddy soil. Compared with the control group,allamendment treatments, except for rice straw biochar, increased the apparent production of ·OH. Considering the dominant role of Fe(I) in ·OH generation,we measured the initial Fe(I) ) content before re-oxidation and its changes during the oxidation process. The generation trend of ·OH was consistent with the consumption trend of Fe(I) ,and both the initial content and consumption of Fe(I ) were positively correlated with the cumulative amount of ·OH,confirming the significant role of Fe(I) in ·OH generation. Furthermore, the application of different soil amendments may influence ·OH generation by affecting the activity of Fe(I) . Comparative analysis of difference in the apparent yield of ·OH in acidified purple paddy soil treated with different soil amendments revealed that Fe(I) ,SOM and the characteristics of the amendments themselves all impacted the ·OH generation. However,the specific pathways and mechanisms of these effects require further investigation.
Key words: hydroxyl radical; soil amendment; purple paddy soil; acidification
羟基自由基(·OH)是氧化能力最强、反应活性最高的活性氧物种,具有强电负性和高氧化电极电位(2.8V) ,可以与绝大部分的生物分子和有机物发生多种不同类型的化学反应[1],在碳和养分循环[2-3]以及污染物降解过程中起着重要作用。(剩余12866字)