酿酒葡萄对盐碱地的适应性评价

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S663.1 文献标识码:Adoi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-204x.2025.10.007
文章编号:1002-204X(2025)10-0041-08
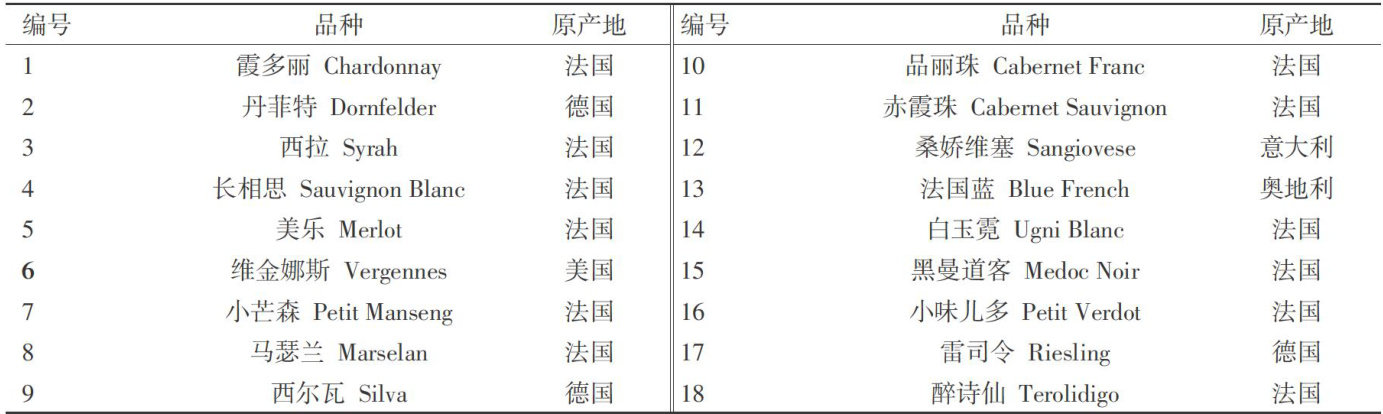
Abstract The wine grape resource garden where the tested varieties are located has severe salinization.By measuring photosynthetic characteristics,the contentof trace elements in different tissuesand other indicators,theadaptability ofdiffrent wine grape germplasm resources tothesaline-alkali environment was evaluated,providing a theoretical basis for the future utilizationof breeding resources.Theresults showthattheaccumulationamounts ofFe indiffrent tissues from largest to smallest are roots,leaves,new shoots,and petioles.The accumulationamountsof Mg in diferent tissues from largest to smalest are petioles,leaves,new shoots,and roots.The accumulation amounts of Mn indiffrenttissuesfromlargesttosmallstareleaves,newshoots,petioles,androots.Theaccumulationamountsof Zn indifferent tisues from largest tosmalest arenew shoots,leaves,roos,and petioles.Theorganizations with the highest accumulation of Ca vary by type.Based on the measured indicators,cluster analysis was conducted on the 18 tested wine grapevarieties.Whenthe square Euclidean distance was 5,theywere clasified into8categories in total. Thetopten varieties in terms of comprehensivescores obtained through principal component analysis are,inorder, ‘Silva''Blue French','Petit Verdot','Medoc Noir','Riesling',‘Marselan','UgniBlanc','Vergennes','Syrah'and 'Dornfelder'.
Key Words Wine grapes;Photosynthetic characteristics; Nutritional elements
我国是葡萄属植物的重要原产地之一,也是世界上葡萄属植物种类最多、种质资源最丰富的国家之_[-2]。(剩余7570字)