淀粉专用型马铃薯表型比较及遗传多样性分析

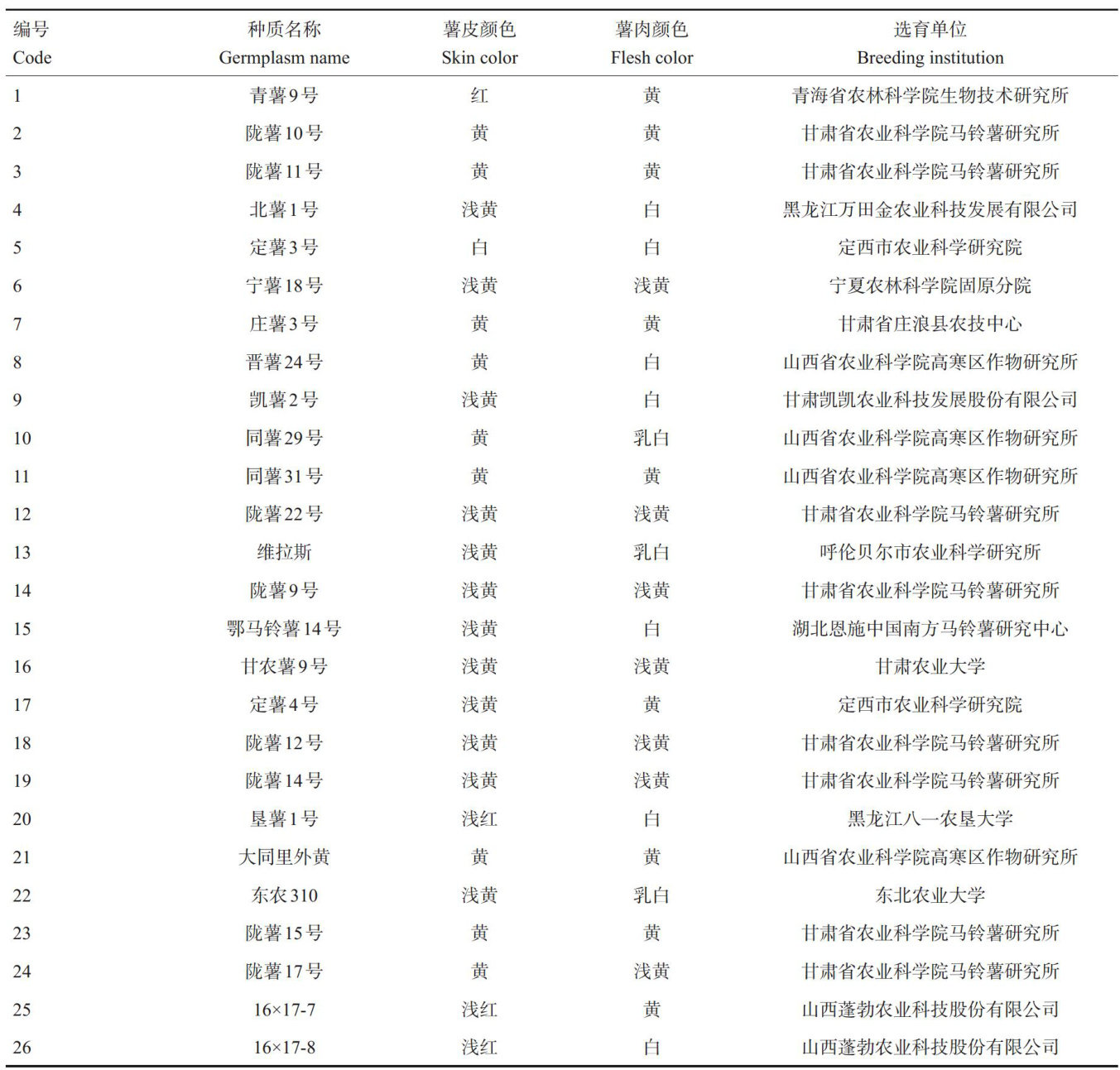
打开文本图片集
Abstract: To clarify the phenotypic differences and genetic relationships of the starch-type potatoes,and to providearesearch basisand breeding materials for the breeding and quality improvement of new varietiesof starch-type potato.This study used26 starch-type potato germplasm resourcesas materials.Through field agronomic trait observation,quality trait measurement,and simple sequence repeats (SSR)marker analysis, genetic diversity was analyzed based on both phenotypic and molecular markers.The results showed that the coefficient of variation of the phenotypic traits ranged from 9.15% to 94.14% ,with the highest coefficient of variation for thenumberof branches,and the lowest coeficient of variation for thedrymater content.The genetic diversity index ranged from 1.71 to2.09,with thehighest genetic diversity index for the number of main stems and the lowest for the number of branches.Based on phenotypic traits,the tested materials were divided into four groups:Group I exhibited high starch content,Group II showed greater plant height and main stem number,Group II was characterized by lower dry mater and starch content,and Group IV performed best in terms of stem thickness and branch number.31 pairs of SSR primers amplified 408 polymorphic loci,with a polymorphic locus rate of 85.18% . On average,each pair of primers amplified 13.16 polymorphic loci,and the polymorphic information content of the primers ranged from 0.1016 to 0.4024.Based on the SSR marker results, the materials were classified into 4 clusters. ClusterI included only Qingshu No.9,with red tuber skin. ClusterI1 contained 22 materials,of which 21 were bred in Gansu,Ningxia,Shanxi,and Heilongjiang,all originating from the northern single-cropping zone. Cluster II consistedof Dingshu No.4,characterized by purple-red tuber eyes.Cluster IV included two introduced materials.The two clustering results showed consistency in the grouping but diferences in the classfication of subgroups.17 materials were classified into the same group under both clustering conditions. Combining phenotypic and SSR markers provides a more comprehensive and accurate reflection of the genetic differences among the germplasm resources.
Keywords: potato;starch-type;quality traits;SSR markers;genetic diversity
马铃薯(SolanumtuberosumL.)起源于南美洲安第斯山脉,适应性广泛,可在全球多个气候区种植,是国家粮食安全的重要保障[1]。(剩余19521字)