两个甘薯野生近缘种的比较基因组分析

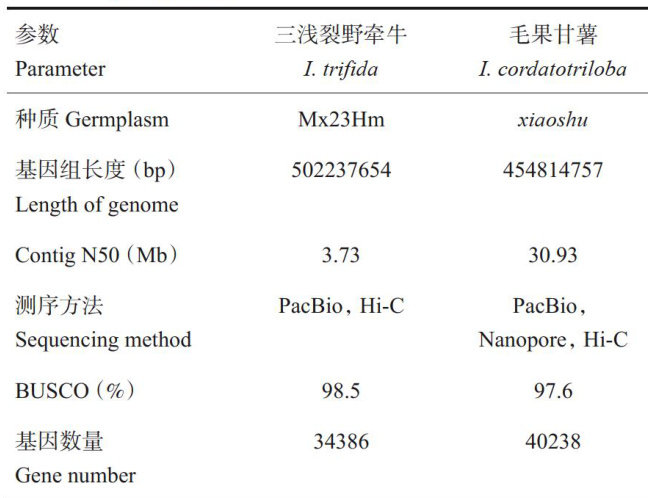
打开文本图片集
Abstract:Sweetpotato is a globally important crop with numerous wild relatives harboring extensive genetic diversity. In this study,a comparative genomic analysis was conducted using two publicly available high-quality genomes of wild relatives. Our analysis identified 1798184 genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs),along with 2076 translocations and 84 inversions encompassing 2106 genes. Enrichment analysis showed that these genes are mainly enriched in pathways such as the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites. Among them,the breakpoints of 34 inversions are located inside the genes and may afect the structure of these genes.There are 10226 insertion-type and 11411 deletion-type structural variations between the two genomes. We anotated these structural variations and conducted gene enrichment analysis on those structural variations that may affect gene function or expression. We found that these potentially affected genes were mainly enriched in pathways of secondary metabolites,while genes related to functions such as DNA repair and replication were enriched.Through deploying statistical results of the synonymous substitution rate (Ks)and fourfold degenerate synonymous site (4DTv)ofcollinear gene pairs of two wild species and other related species,it was indicated that the common ancestor of the genus Ipomoea diffrentiated into different species after a whole-genome triplication event.Collectively,the findings will provide insights for the excavationof excellent variations ir wild relatives of sweetpotato as well as for analyzing species differentiation
Keywords:sweetpotato;wild relatives;comparative genomics
作物的野生近缘种蕴含着丰富且有价值的基因资源,不仅可以弥补栽培种长期驯化过程中丢失的重要性状,还可以为栽培作物的起源和驯化提供重要的遗传信息[1。(剩余16777字)