改进RetinexNet的低光照图像增强方法

打开文本图片集
中图分类号: TP391 文献标志码:A DOI:10.13338/j.issn.1674-649x.2025.02.010
Low-light image enhancement method based on improved RetinexNet
GU Meihua,DING Mengyue ,DONG Xiaoxiao (School of Electronics and Information,Xi'an Polytechnic University,Xi'an 71o048,China)
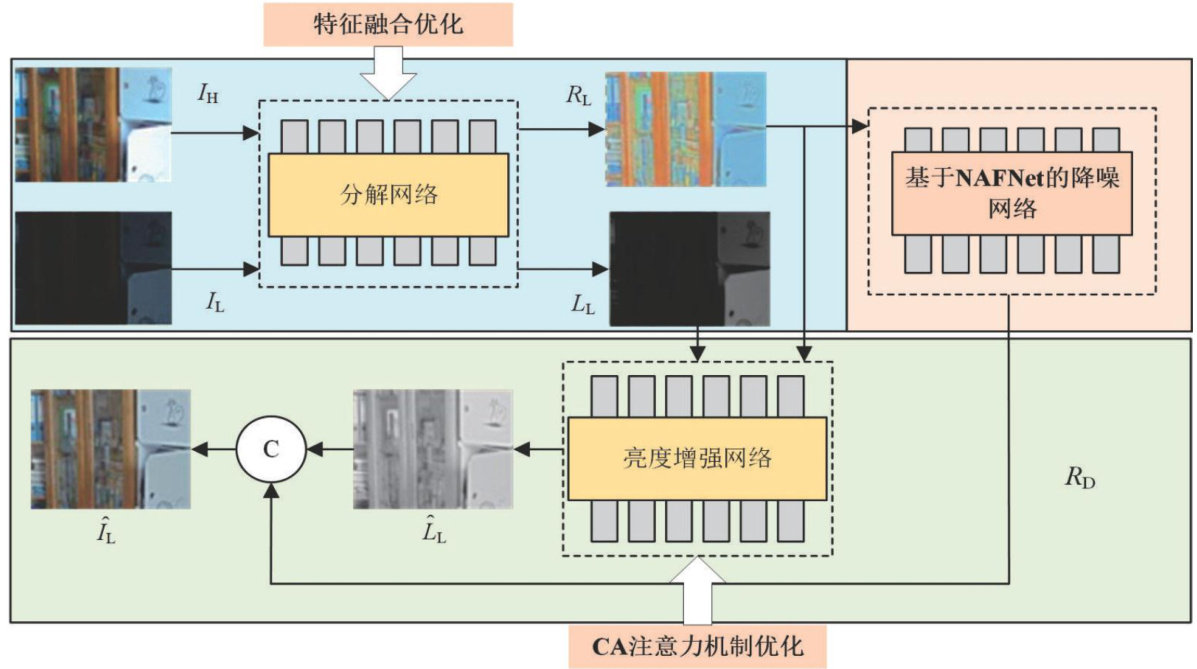
AbstractUnder low-light conditions,images often suffer from loss of details and increased noise,which seriously affects the image quality. Therefore,this paper proposes a low-light image enhancement method incorporating an attention mechanism.Base on RetinexNet model,first,in the decomposition network,more feature information and details were retained by introducing a feature fusion module,which connected the shallow features horizontally and input them into the deep network. Secondly,to address the problem of high noise in the reflection component,the NAFNet noise removal module was added to the noise reduction network,which effectively reduced the impact of noise on image quality.Finally,in the luminance enhancement network,the Unet structure was adopted and the channel attention(CA) was embedded,which enabled it to learn the correlation between different feature channels and the feature representation of a specific channel under different lighting conditions,thus significantly improving the enhancement effect of the illumination map. The experimental results show that compared with RetinexNet,the method in this paper has significant improvement in various indexes.Specifically,the peak signal-to-noise ratio is improved by about 1.O5 dB,the average absolute difference is improved by about 0.03,the structural similarity is improved by about O.O9,the image similarity is improved by about 0.05, and the natural image quality is improved by about O.75. In summary,the method in this paper can effectively suppress noise and significantly improve the enhancement of low-light image details.
KeywordsRetinexNet; feature fusion; low-light image enhancement; convolutional neural network;channel attention
0引言
低光图像增强(low-lightimageenhancement,LLIE)是计算机视觉领域的一项关键且具有挑战性的任务[1],其目的是提高低光场景下的可见度和对比度,包括不均匀光照[2]、极端黑暗[3]、背光场景[4]和夜间拍摄[5]等。(剩余14948字)