玻化微珠空心砌块热工性能模拟及其用于建筑外墙的节能分析

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TU528 文献标志码:A 文章编号:2097-3853(2025)03-0228-08
Abstract:Inorder to solve the problems of high thermal conductivityand high moisture absorption of traditional block materials,the vitrified microbead cement-based material with low moisture absorption were prepared in this study,and the moisture absorption of standard curing room for 7 consecutive days and the change rule of thermal conductivity after moisture absorption were tested.At the same time,based on onedimensional steady-state heat transfer theory,the thermal performance of the block was simulated by ABAQUS,and the thermal analysis of the building was conducted by ECOTECT. Test results show that the thermal conductivityof vitrified microbead cement is low,and itcan significantlyreduce the heat flux intensity and temperature on the inner surface of the block,as well as effectively increase the thermal resistance of the block,so as to improve the thermal performance of the block,and effectively reduce the influence of humid environments.The vitrified microbead block used for building exterior wals can reduce building energy consumption,as well as the heating,ventilation,and air conditioning(HVAC)load,fabric gains and losses (FABRIC)value,and passive component heat gain and loss,and the exterior wall can stilleffectively reduce building energy consumption and maintain building comfort after moisture absorption.
Keywords: hollow blocks;thermal performance; vitrified beads; building energy consumption
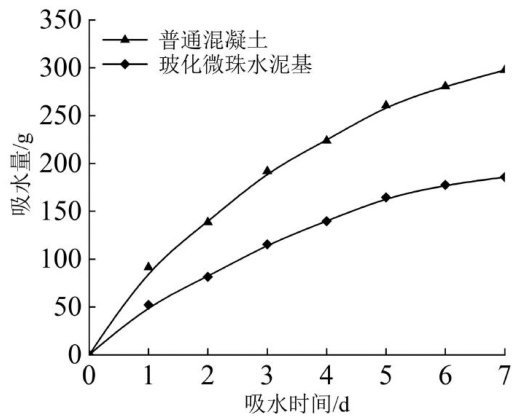
东南沿海地区属于典型的热湿气候区,显著的风驱雨(WDR)现象易引起建筑外墙渗水、墙体材料劣化等问题,外墙受到水侵蚀时热工性能降低,其建筑能耗势必会受到影响,因此国内外学者针对热湿传递对建筑能耗的影响进行了大量研究。(剩余9307字)