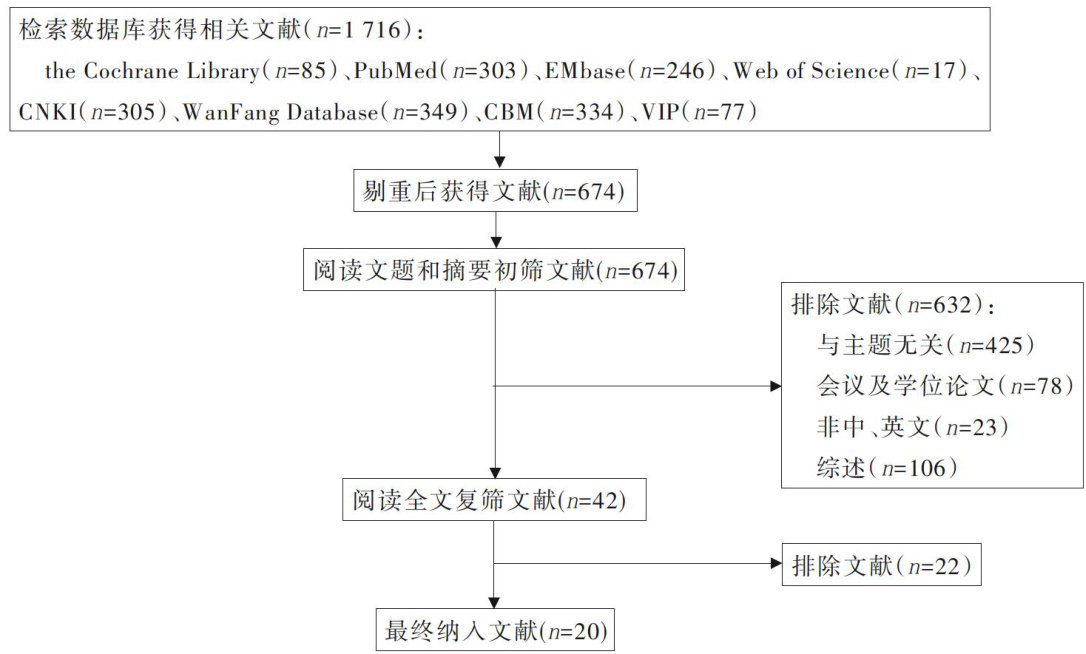
神经肌肉电刺激预防住院卧床病人深静脉血栓形成效果的Meta分析

打开文本图片集
AbstractObjective:Tosystematicallevaluate theefectof neuromuscularelectrical stimulation (NMES)inpreventingdepvein thrombosis(Dinospitalieddriddenpatints,ndtopovideevidecebasedevenefrthelcalprevetionofthuef venous thrombosis.Methods:TheliteratureonthepreventionofDVTinpatientsbyNMESwasretrievedfromPubMed,theCochrane Library,WebofScience,EMbase,CNKI,WanFang Database,VIPandCBM.Thesearchperiodwasfromtheestablishmentofthe databasetoJulyO24.Literaturesrening,dataextractionandqualityevaluationwereindependentlyconductedbytworesearchrs accordingtotheinclusionandexclusioniteriaRevMan5.4softwarewasadoptedforMetaanalysis.Results:Atotalof2Oartisere included.The results of the Meta-analysis showed that NMES could reduce the incidence of DVT(RR =0.45 95% CI 0.35-0.58, P<0.00001 ! accelerate the venous blood flow of the lower extremities MD=4.59,95%CI3.40-5.78,P<0.00001) ,reduce the D-dimer level of patients (SMD=-2.64,95%CI-3.83-1.44,P<0.0001) ,and alleviate pain(MD=-1.23,95%CI-1.43-1.04,P<0.00001) .Conclusion: ExistingevidenceshowsthatNMEScanpreventDVinpatients,utthequalitylevelofteliteratureisnothighHigqualityliical studies are still needed to further verify and analyze its efficacy.
Keywordsneuromuscular electrical stimulation; deep vein thrombosis; Meta-analysis; evidence-based nursing摘要目的:系统评价神经肌肉电刺激(NMES)在住院卧床病人预防深静脉血栓形成(DVT)中的效果,为临床预防静脉血栓的发生提供循证依据。(剩余13053字)