运动干预对维持性血液透析病人衰弱影响的Meta分析

打开文本图片集
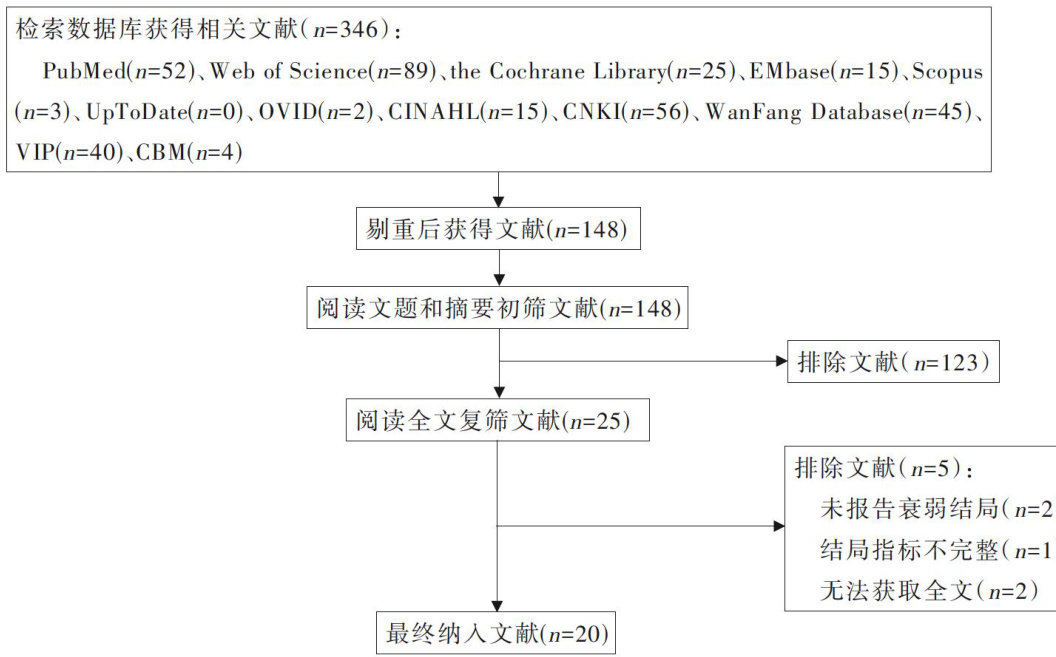
AbstractObjective:Toevaluatetheinterventioneffectofexerciseinterventiononfrailtyinmaintenancehemodialysispatients. Methods:Theliteratureontheefectofexerciseinterventiononthefrailtylevelofmaintenancehemodialysispatientswasretrievedfrom databases suchas PubMed,WebofScience,CNKI,and WanFang Database.The search periodwas from the establishmentof the databasetoNovember224.Literaturesrenng,dataetractionandalityevaluationwereindependentlyconductedbytwoacrs. RevMan5.4softaresdptedretaanalsisResults:Atotalof2rticlesrecudednoling1475patient.esulsfte Meta-analysis show that exercise intervention can effectively improve the frailty state of patients(SMI )=-1.19,95%CI-1.74-0.64 , P<0.000 1 ).The results of subgroup analysis showed that aerobic resistance exercise(SMD ⋅1=-1.30,95%CI-2.19AA-0.41,P=0.004 ) with continuous intervention for l2 weeks(SMD =-1.92,95% CI -2.83--1.01, P=0.000 3),an intervention frequency of 2 or 3 times per week(SMD =-1.13 , 95% CI -1.80--0.45 , P<0.000 01 ),and a single exercise duration of ⩽30 minutes(SMD=-1.34, (204号 95% CI—2.21-—0.47, P<0.000 01 ) improved the frailty state of MHD patients better,and the difference was statistically significant. Conclusions:Existing evidence shows exerciseinterventioncanefectivelyimprovedthefrailtystateofMHDpatients.Continuous intervention for12 weeks,2 or 3 times per week,with each session lasting ⩽30 minutes,aerobic resistance exercise may havea better effect in improving the frailty of MHD.
Keywordsexercise intervention; maintenance hemodialysis; frailty; Meta-analysis; evidence-based nursing摘要目的:评价运动干预对维持性血液透析病人衰弱影响的干预效果。(剩余8691字)