院内及院外功能锻炼对ICU后综合征病人影响的Meta分析

打开文本图片集
Abstract Objective:To systematically evaluate the influence of in-hospital and out-of-hospital functional exercise on patients with post-intensive care syndrome.Methods:Randomized controlled trials on the influence of in-hospital and out-of-hospital functional exercise of patients with post-intensive care syndrome were searched from the Cochrane Library,PubMed,Web of Science,EMbase,CBM,CNKI,WanFang Database,and supplemented by manual retrieval.Meta-analysis was performed by using RevMan 5.3 software.Results:A total of 14 randomized controlled trials were included.Meta-analysis results showed that in-hospital and out-of-hospital functional exercise could effectively improve the physiology of patients at 2 to 3 months and 6 months after discharge,mental health and anxiety at 6 months,cognitive function at 3 months,the difference between the intervention group and the control group was statistically significant(P<0.05).But the difference of depression between the two groups was not statistically significant(P>0.05).Conclusion:Current evidence shows that in-hospital and out-of-hospital functional exercise can effectively improve the long-term physiology,mental health,anxiety and cognitive function of ICU patients,but the effectiveness of depression and long-term effects still needs further studies to verify.
Keywords post-intensive care syndrome;ICU survivors;functional exercise;Meta-analysis;evidence-based nursing
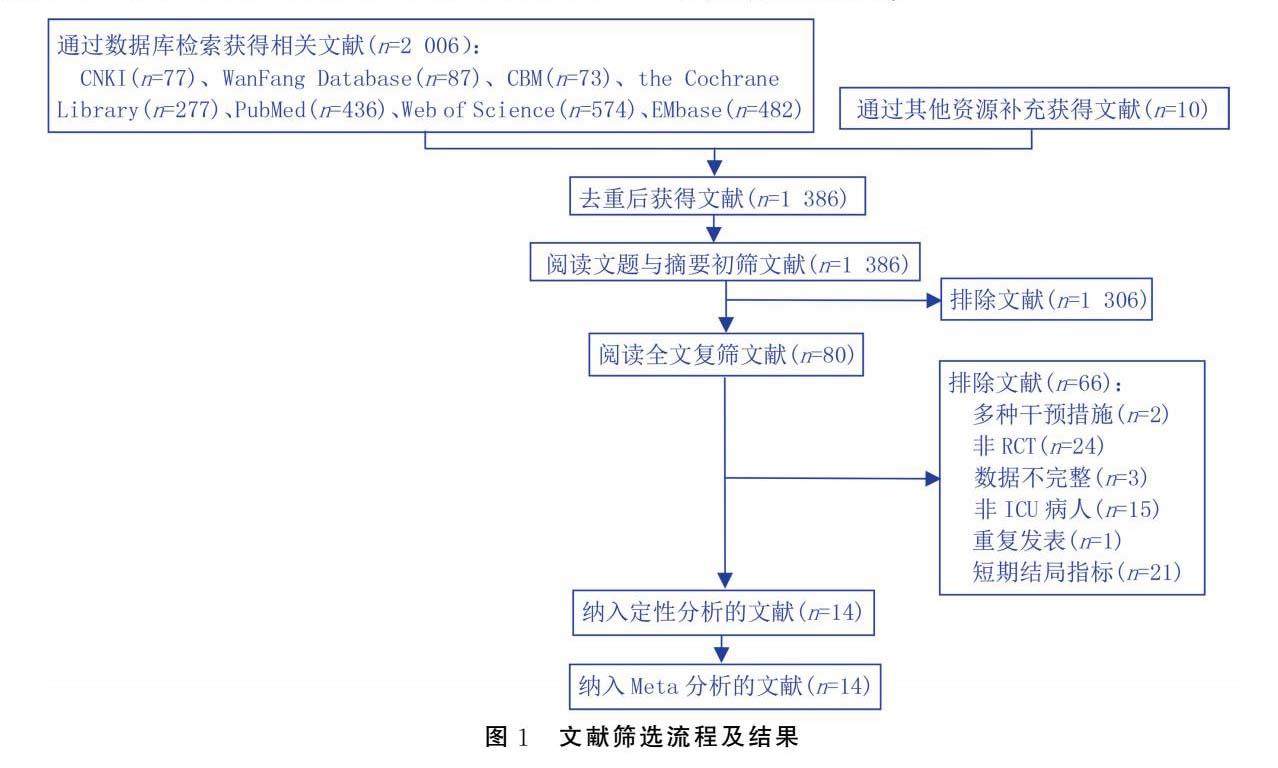
摘要 目的:系统评价院内及院外功能锻炼对重症监护室(ICU)后综合征病人的影响。(剩余17813字)