制造业作业人员长工时与睡眠障碍的关系研究:饮酒与心理健康的作用

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:R135.99 文献标志码:A DOI:10.7652/jdyxb202504021
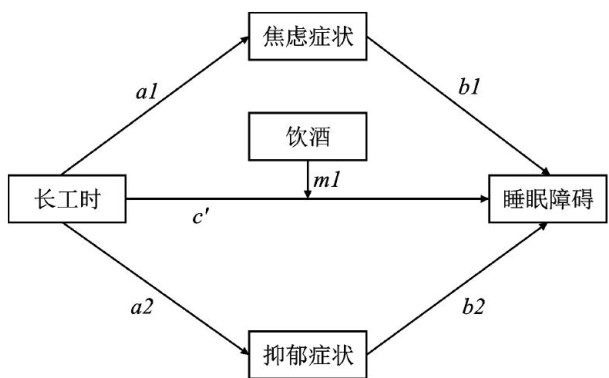
ABSTRACT: ObjectiveTo assess the impact of long working hours on sleep disorders among manufacturing workers and explore the roles of alcohol consumption and mental health factors (anxiety and depresive symptoms) in this association.MethodsA cross-sectional study design was used to survey1 336 manufacturing workers in Shenzhen.Wecolected the data of their demographic characteristics,work-related factors,personal behaviors, sleepdisorders,and mental health status.MultivariateLogistic regression analysis wasused toasssthe association between long working hours and sleep disorders.Stratifiedanalysis and mediation effect models were aplied to examine the efect modification by alcohol consumption and the mediating role of mental health factors, respectively. ResultsAmong the study samples, 31.8% reported long working hours and 45.6% had sleep disorders.Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that long working hours significantly increased the risk of sleep disorders (adjusted OR=2.073 , 95% CI :1.478—2.907, P<0.001 ).Stratified analysisrevealed that the association between long working hours and sleep disorders was more pronounced among alcohol consumers (adjusted OR=2.556 , 95% CI :1.432—4.562, P=0.001 ).Mediation effect analysis showed that anxiety and depressive symptoms partially mediated the relationship between long working hours and sleep disorders,with indirect effects accounting for 25.71% and 27.14% ,respectively. ConclusionLong working hours increase the risk of sleep disorders among manufacturing workers,particularly among those who consume alcohol. Anxiety and depressive symptoms partially explain the association between long working hours and sleep disorders.
KEY WORDS: manufacturing industry; long working hours; sleep; effect modification; mediation
睡眠障碍是由多种因素引起的睡眠节律紊乱,其表现为睡眠质量下降和睡眠行为异常,并对个体的身心健康产生不利影响[。(剩余12869字)