聚合物固体电解质在金属锂电池中的研究进展

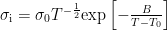
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:O646;TG146.2 文献标志码:A
文章编号:2096-2983(2025)03-0011-08
Abstract: Li metal battries have attracted significant attention due to their high energy density. However, safety issues arising from Li dendrite growth have limited their practical application. Solid electrolytes can significantly inhibit dendrite growth and exhibit excelent safety. In particular, solid polymer electrolytes are flexible, easy to process, and amenable to large-scale production, making them the most promising electrolyte systems.Nevertheless, solid polymer electrolytes are constrained by their low ionic conductivity and narrow electrochemical window, which prevent them from meeting practical application requirements. Therefore,the design and optimization of solid polymer electrolytes are of great significance. This article reviews the Li+ transport mechanisms, preparation methods, and modification strategies of solid polymer electrolytes and provides an outlook on the future practical application of solid state Li metal batteries.
Keywords: solid polymer electrolytes; solid state Li metal battery; ionic conductivity; Li dendrite
随着化石能源的日渐枯竭,以及新能源汽车等领域的快速发展[1],开发具有高能量密度的电化学储能器件具有重大意义[2]。(剩余15243字)