施氮改变了三江平原湿地小叶章对 CO2 升高的生理响应

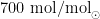
打开文本图片集
关键词: CO2 浓度升高;施氮;叶片氮;小叶章;光合作用中图分类号:S718.5;S153;X131.1 文献标识码:A文章编号:1001-9499(2025)04-0040-06
Nitrogen Application Changed the Physiological Response of Calamagrostis angustifolia to Elevated CO2 in Sanjiang Plain Wetland
WANGJianboFUXiaoling LIU Yingnan ZHONGHaixiu** (Institute of Natural Resourcesand Ecology,Heilongjiang Academy ofSciences,HeilongjiangHarbin )
AbstractAmbient or elevated CO2 concentration (400,550 and 700μmol/mol )andNapplication (O and 8gN/m2⋅y, ,low N,high N,respectively) were set up in an open-top chamber (OTC) to study the potential responses of Calamagrostis angustifolia in Sanjiang Plain wetland with different soil N availability.N application strongly increased leaf soluble protein content in different CO2 treatments,increased leaf nitrogen content under elevated CO2, and decreased leaf starch content and leaf C/N ratio under elevated CO2 Elevated CO2 concentration significantly reduced leaf nitrogen content under both CK and HN treatments.Nitrogen fertilization not only alleviated the decreaseofleaf nitrogen content,butalsomediated the increase of leaf C/N under elevated CO2 In both CK and HN treatment, the net photosynthetic rate (Pn) in June increased under elevated CO2, however,the increase of net photosynthetic rate was significantly higher in HN treatment than that in CK treatment.In July and August,Pn decreased with the increase of CO2 concentration,which may be due to photosynthetic adaptation caused by long-term CO2 fumigation. N applicationnotonlysignificantlydecreasedthe trend,butalsosignificantly increased leafnetphotosynthetic rate.Atthe end of the growing season,N fertilization significantly increased the biomass of plants growing in different CO2 conditions,especiallyat
Key wordsNapplication; elevated CO2 ;leafN;Calamagrostis angustifolia;photosynthesis
大气中二氧化碳浓度升高和氮沉降一直是全球变化研究中的重要问题。(剩余9529字)