医护人员心理弹性量表的汉化及信效度检验

打开文本图片集
Chinese version of Medical Professionals Resilience Scale and its reliability and validity test
JIAO Chunhui, QU Qingrong, CUI Tianjiao, GAO Yage, GAO Yaxin
The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Henan 450052 China
Corresponding Author QU Qingrong, E⁃mail: qqr890524@163.com
Abstract Objective:To translate the Medical Professionals Resilience Scale(MeRS) into the Chinese,and to test its reliability and validity among medical staff.Methods:MeRS was translated and back⁃translated according to the Brislin translation model,and the Chinese version of MeRS was adjusted and revised through expert consultation and pre⁃investigation.The convenience sampling method was used to select 474 medical and nursing staff from a tertiary grade A hospital in Zhengzhou to conduct a questionnaire survey to evaluate the reliability and validity of the Chinese version of MeRS.Results:The Cronbach's α coefficient of Chinese version of MeRS was 0.961.And the Cronbach's α coefficient of each dimension ranged from 0.864 to 0.924.The test⁃retest reliability was 0.918.And the test⁃retest reliability of each dimension ranged from 0.803 to 0.876.The Scale⁃Content Validity Index(S⁃CVI/Ave) was 0.942.And the Item⁃Content Validity Index(I⁃CVI) ranged from 0.857 to 1.000.Exploratory factor analysis extracted 4 common factors,and the cumulative contribution rate of variance was 62.281%.With the Chinese version of the Connor⁃Davidson Resilience Scale as the criterion,the correlation value of the criterion was 0.873(P<0.01).Conclusion:The Chinese version of MeRS had good reliability and validity,and could be used to measure the resilience of medical staff in China.
Keywords medical staff; psychological resilience; reliability; validity
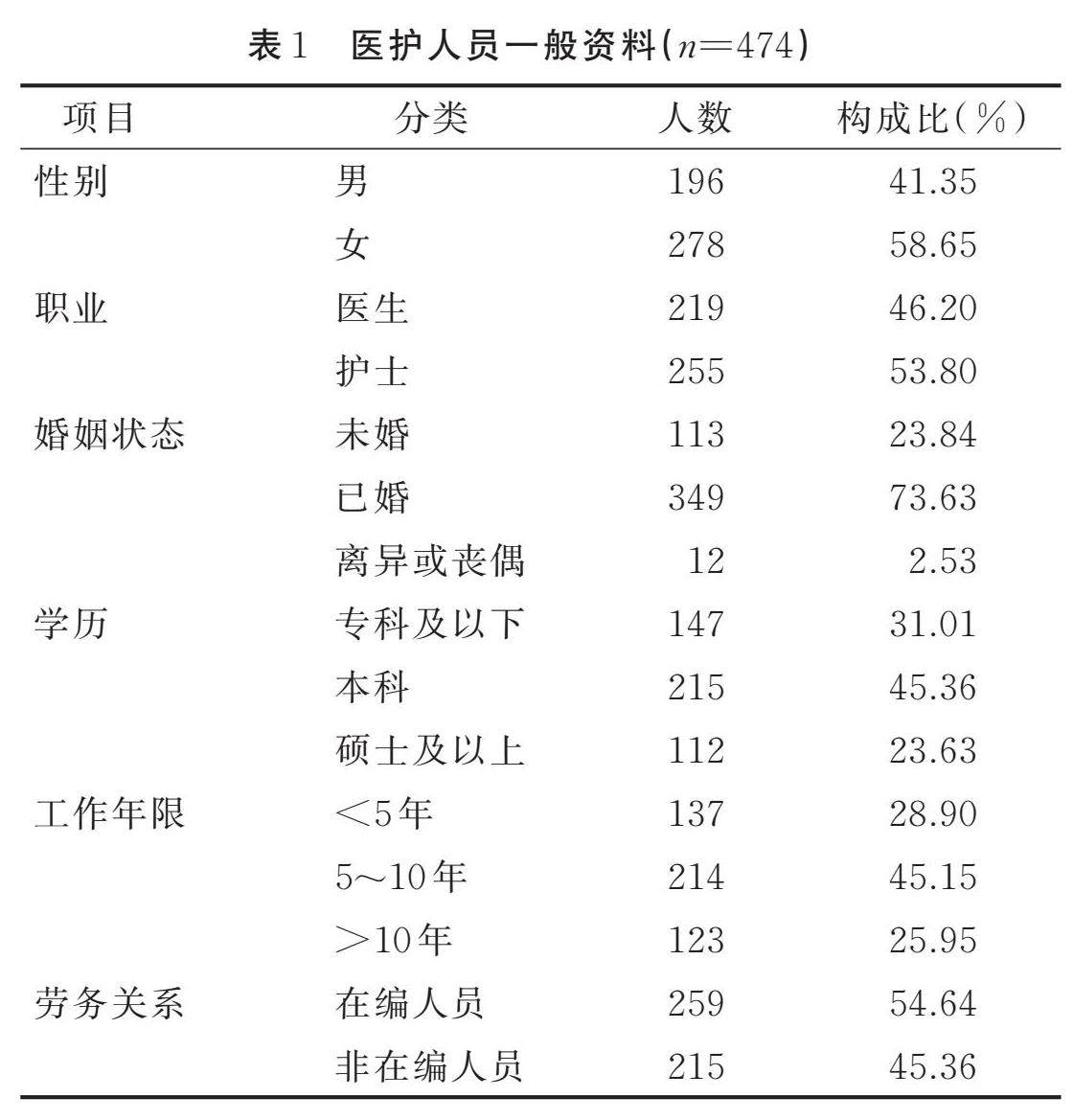
摘要 目的:对医护人员心理弹性量表(Medical Professionals Resilience Scale,MeRS)进行汉化,并在医护人员中检验其信效度。(剩余8929字)