基于临床病症特点的肝纤维化动物模型评价分析

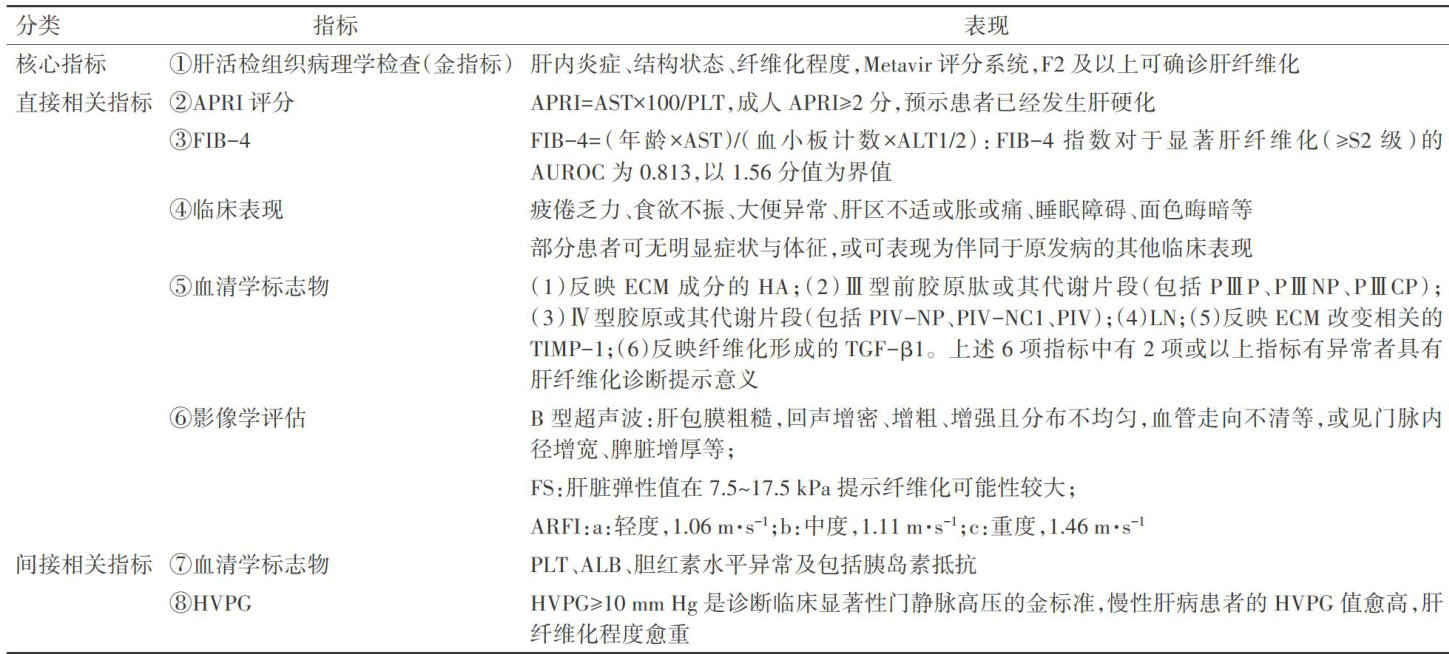
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:R-332;R285.5 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1003-9783(2025)09-1555-11
doi: 10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2025.09.014
Evaluation and Analysis of Liver Fibrosis Animal Models Based on Clinical Characteristics
QIN Zehua’,ZHU Xinyun¹, ZHU Ye²,TANG Songqi³,DU Donglian¹,QIU Feifei,HUANG Wei'(1. Chengdu Universityof Traditional Chinese Medicine,Chengdu Sichuan,China;2.TheFirst Afiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University,Haikou 571199 Hainan,China;3.Hainan Medical University,Haikou 571199 Hainan, China;4. Chengdu Qihuang Born biological technology Co.,LTD,Chengdu Sichuan,China)
Abstract:Objective To explore thepathogenesis of liver fibrosis andanalyze thecharacteristics of existinganimal models basedon clinical features,with theaim of proposing improvementsand identifying more accurate modeling approaches.Methods Literature on liver fibrosisand itsanimal models was reviewed to analyze the etiology, pathogenesis,diagnostic criteria,and the alignment between modelreplication methods (including model subjects and techniques)and clinical manifestations.Results The carbon tetrachloride ( CCl4 )-induced intraperitoneal injection model i mice demonstrated the highest consistency with clinical features.Conclusion Current liver fibrosis models predominantlyuse rodents,which exhibit limitations in replicating clinical conditions.Future research should prioritize non-humanprimate modelsand refine evaluation standards to develop animal models that more precisely mirror clinical characteristics,thereby advancing therapeutic studies for liver fibrosis.
Keywords: liver fibrosis;clinical characteristics;animal models;clinical concordance
肝纤维化(liverfibrosis,LF)是一个动态的、高度整合的分子、细胞和组织过程,主要是由于交联的I型胶原(collagenI,ColI)和Ⅲ型胶原(collagenII,Col II)等细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)
进行性过度积累。(剩余19697字)