患者来源免疫维持肿瘤类器官的兴起、发展及其在膀胱癌治疗中的应用

打开文本图片集
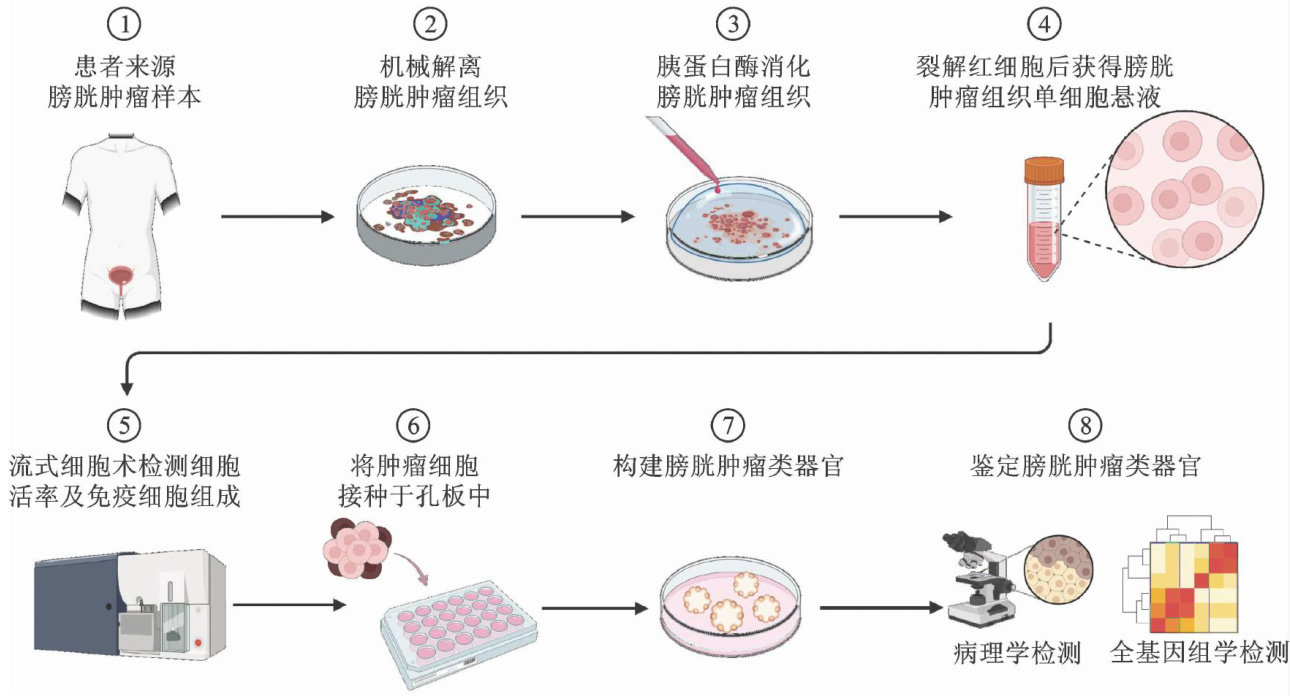
ABSTRACT:In recent years,patient-derived tumor organoid (PDTO)models have rapidly emerged as important tools in cancerresearch,thanks totheirunique abilityto preservethecharacteristicsof primarytumors.These models provideareliable preclinicalresearch platformforscreening individualizedchemotherapyand targeted therapiesforpatients.However, traditional PDTOs lack immunecelsand cannot replicate the tumor immune microenvironment,which restricts theirutilityin evaluating immunotherapies.Toaddressthischallenge,researchers havedevelopedcomposite models thatincorporateboth tumor cells and immune cels,known as patient-derived immunocompetent tumor organoids(PDITOs).PDITOs have shown excelent performance inthe preclinicalevaluationof immunotherapies,particularlywithPD-1/PD-L1immune checkpoint inhibitors,with some studies reporting up to 100% accuracy in predicting patient responses to immunotherapy.As a common malignancy of theurinary system,bladder cancer has benefited from the applicationof PDITOs in drug screning and personalizedimmunotherapyevaluation,demonstrating significant potential.This paperaimstoreview theriseanddevelopment of PDITOs,andcompare the advantages andlimitations of usingdiferent methods toconstruct PDITOs,soas to explore their application in the treatment of bladder cancer.
KEYWORDS:organoid;patient-derived immunocompetenttumororganoid;bladercancer;personalized medicine;immunotherapy摘要:患者来源的肿瘤类器官模型因保留原发肿瘤特征的独特优势迅速成为近年癌症研究应用的重要工具,为患者个体化的化疗药物和靶向药物的筛选提供了可靠的临床前研究平台。(剩余14005字)