闽江流域土壤湿度及其记忆性的时空特征与趋势分析

打开文本图片集
Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Trend Analysis of Soil Moisture and Its Memory Effect in the Minjiang River Basin
YIN Fangxu¹, YOU Jiewen1,23*, ZHANG Yinchi³, WU Jingwen GAO Lu 1,2,3 (20号 (1.InstituteofGographyujianoalUiversityuzhou3517na;2.KeyLboratoryforHuidubroicalEo geographicalProcesesofheistryofEducationFuanalUivesityuzhou517,ina;3.holofaial Sciences,FujianNormalUniversity,Fuzhou 35O117,China)
Abstract:Thisstudyinvestigatedthespatiotemporaldiferentiationcharacteristicsofsoilmoistureanditsmemoryefectnthe MinjiangRiverBasinimingtoprovideasientificbasisforaterresouresmanagement,aswellasfloodpreventionanddisaster reductioinumidregiosBasedonakgridailyscalesoiloisturedataset(o2O22)regresiofitingndutoeaion coeffcientmetodswereplidtostematicallynalethspatialgadint,interaalvaation,sasoaldamics,andory efectsof Soilmoistureinthebasin.SoilmoistureintheMinjiangRiverBasinexibitsasignificantnorthwestsoutheastdecreasing trend,with high-value zones (>0.43m3/m3 )concentrated in the Wuyi Mountain Forest Ecological Zone and low-value zones (<0.39m3/ m³) distributed along the coastal urbanized plains. Seasonal dynamics reveal a spring peak (0.44m3/m3 )and a decline to 0.39m3/m3 in autumn.Thememoryefectsofsoilmoistureatdiferentdepthsshowspatialdiferentiationcharacteristics,andthememorytimeof depsoilinthelowerreachesoftheMinjiangRiverislowerthan3Odays.ThesoilmoistureintheMinjiangRiverBasinshows spatiotemporalditiatioemorectsmontatedeptspaceterogeityltingesesguto offactorssuchasprecipitation,temperature,ndvegetationcoverage.Thefindingsenhancetheunderstandingofsoilmoistureand provide implications for flood warning and water resource management in the Minjiang River Basin. Keywords: soil moisture; soil moisture memory;spatiotemporal diferentiation; variation trend; Minjiang River Basin
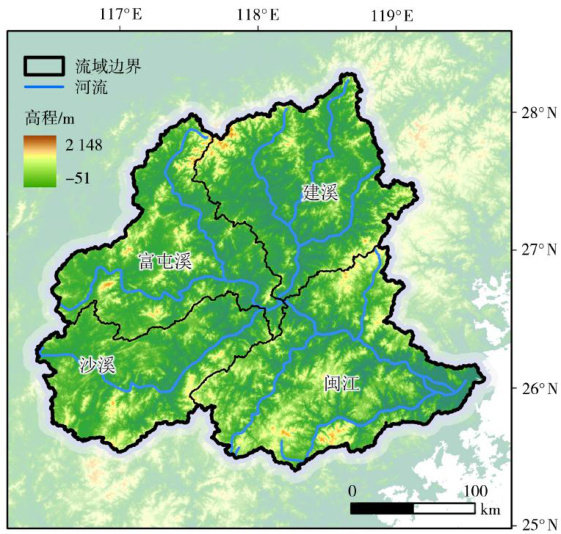
王壤湿度作为陆地生态系统与大气相互作用的关键变量,在能量和水分循环中发挥着至关重要的作用,其通过影响地表蒸散发、水分再分配及土壤热容量,进一步调控局地、区域乃至全球的气候系统[1-4]。(剩余16558字)