我国长期处方服务对高血压患者管理效果的Meta分析

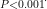
打开文本图片集
【中图分类号】R544.1 【文献标识码】A
【Abstract】 Objective To systematically review the manage effects of prescription refill in hypertension management in our country,and to provide suggestions for chronic disease policies. Methods Web of Science,PubMed,Embase, Cochrane Library, SinoMed, CNKI, WanFang Data,VIP databases were electronically searched to collect randomized controlled trails (RCTs) of prescription refill services for hypertension management from inception to March 31,2024. Two reviewers independently screened the literature,extracted data and assessed the risk of bias of the included studies. Meta-analysis was conducted by using RevMan 5.3 software. Results
A total of 14 RCTs involving 1,386 patients were included. Meta-analysis results showed that systolic blood pressure [MD =-9.19 , 95%CI (-12.20, -6.17), P<0.001 ],diastolic blood pressure [MD=-4.98 , 95%CI (-6.71, -3.26), in experimental group was significantly lower than the control group. Patient compliance score[SMD =2.05 95%CI (0.44, 3.66), P=0.01 ], compliance rate[RR :=1.15 , 95%CI (1.08,1.23), P<0.001i l,patient satisfaction[RR .=1.28 , 95%CI (1.16, 1.42), P<0.001i in experimental group were significantly higher than the control group. Conclusion The prescription refillfor chronic diseases is rapidly developing in our country,and has achieved remarkable results in the management of hypertension patients.In the future,it is necessry to further promote the safe,efective and standardized implementation of prescription refillservices,and carry out high-quality service models with multi-disciplinary participation.
【Keywords】Hypertension; Prescription refill; Manage effect; Meta-analysis
心血管疾病在我国城乡居民疾病死亡构成比中占首位[1,高血压是最常见的心血管疾病,我国政府和专业组织实施了一系列措施提升高血压防控水平,明显改善了高血压的知晓率、治疗率和控制率,但总体仍处于较低的水平,患病率仍呈逐渐上升趋势[2。(剩余16381字)