基于FAERS数据库的药物相关乙型肝炎病毒再激活信号挖掘与分析

打开文本图片集
【中图分类号】R373.2 【文献标识码】A
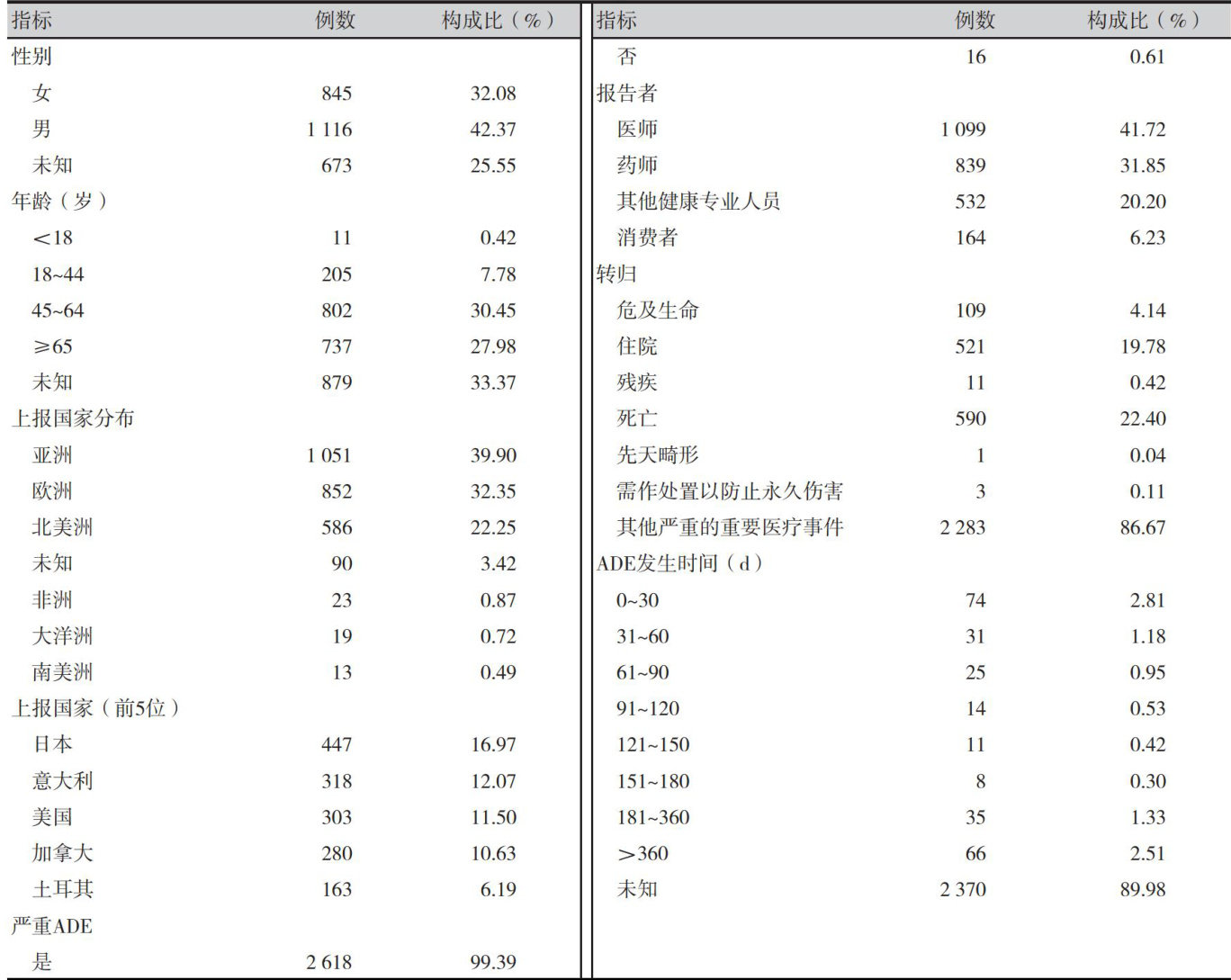
【Abstract】 Objective To conduct data mining on drugs causing hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation based on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration's Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database,and to provide reference for safe clinical drug use. Methods Adverse drug event (ADE) report data with HBV reactivation were screened using data from the FAERS database from the first quarter of 2004 to the second quarter of 2024,and the correlation between drugs and HBV reactivation signals was analyzed by signal detection using the reporting odds ratio (ROR) method and the Bayesian confidence progressive neural network (BCPNN) method. Results A total of 2,634 ADE reports related to HBV reactivation were collected, with a higher proportion male patients (42.37%) )than female (32.08%) , and the age was mainly concentrated in the 45-64 years old (30.45% ). The main reporting country was Japan. A total of 70 drugs that could trigger HBV reactivation signals were detected,of which 50 had no mention of the risk of HBV reactivation in their instructions and 45 had no mention of the risk of HBV reactivation in the Livtox database. The drug classes were dominated by antineoplastic drugs and immunomodulatory drugs, including 34 drugs used for the treatment of hematological neoplasms. Rituximab had the highest number of reports among the drugs associated with HBV reactivation. Conclusion Multiple new pharmacovigilance signals which cause HBV reactivation are found in this study. Antineoplastic drugsand immunomodulatory drugs are high-risk drugs,and should be emphasized in clinical use to strengthen the monitoring of hepatits B surface antigen and HBV-DNA, and to take timely interventions to ensure the safe use of drugs.
【Keywords】Adverse drug event; FAERS database; Hepatitis B virus reactivation; Signal mining Pharmacovigilance
乙型肝炎是由乙型肝炎病毒(hepatitisBvirus,HBV)导致的疾病,给我国造成了巨大的经济负担[。(剩余13922字)