基于BSA-seq的高粱柄伸长度QTL定位

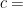
打开文本图片集
Abstract:[Objective]Thisstudy aimed to identify quantitativetrait loci(QTL)asociated with sorghum peduncle length using BSA-seq technology,screen sorghum plants with excellent peduncle elongation traits,and provideatheoretical basis for improving elite sorghum backbone lines and breding mechanization-adapted varieties.[Methods]The studyused sorghum maintainer lines 7O5OB(short peduncle)and Tx2925B(long peduncle),along with their F 2 population derived from emasculated hybridization.Peduncle length was measured in parents and thesegregating population.Two bulked pools,EL-L(long peduncle)andEL-S(shortpeduncle),wereconstructed forQTLmapping.[Results]Thepeduncle lengthof 7O50Bwassignificantly shorter than that of Tx2925B ,with a phenotypic variation coeficient variation of 76.1% in the F2 population. SNP variations detectedinEL-L,EL-S,7O5OB,and Tx2925B were1574836,2041538,2512 953and688446 respectively.Ata 99% confidencelevel,16QTLswereidentifiedonchromosomes1,4,5,8and1O,including9onchromosome1,4onchromo some4,andleachonchromosomes5,8and10.Thecandidate intervalscontained2 to1,40lgenes,with 2748and1779 transcriptsannotated inGOandKEGGdatabases,respectively.[Conclusion]Thisstudy identified16QTLssignificantlyasso ciated with peduncle length across five sorghum chromosomes,providing candidate gene resources for deciphering the genetic
mechanismsofpeduncleelongation.Thesefindingsestablishamolecularfoundation forbreeding mechanized sorghumvarieties and improving elite germplasms.
Keywords:Sorghum,Peduncle Elongation Length,Genetic Analysis,QTL
高粱作为全球第5大禾谷类作物,在食品、饲料、酿造等行业应用广泛[1]。(剩余13997字)