杭州市3\~6岁儿童乳牙患龋现状分析

打开文本图片集
Analysisof thecurrent situationofcaries in thedeciduous teethof childrenaged 3-6years in Hangzhou
Li Li,Xu Hong,Liu Xuda
Departmentof healthhazardssurveillance(DHHS),Hangzhou CenterforDiseaseControlandPrevention (Hangzhot
HealthSupervisionInstitution),Hangzhou3loo21,China
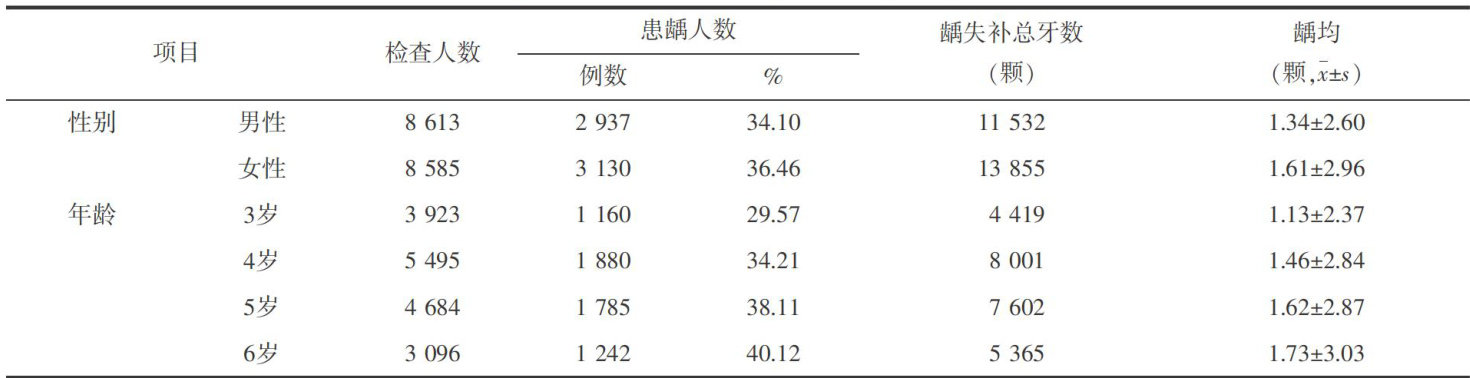
【Abstract】Objective To analyzethe situationof caries inthe deciduous teethofchildren aged 3\~6 years old in Hangzhou,and toprovideabasis for thedevelopmentandimplementationofcomprehensivecaries interventions for preschool children in Hangzhou.MethodsOral examinations were conducted on17198 children in Hangzhou from 2O2O to 2O22.And the results of these examinations were collected and analyzed.ResultsThe caries pre-valencerateof deciduous teeth of children aged3 to6 in Hangzhou is 35.28%(6 O67/17198),with a mean number ofcariousteth of (1.48±2.79);;thecaries prevalencerate of girls is higherthan thatofboys;the caries prevalencerate increases gradualywith age;thereare diffrences incaries prevalence rates among different tooth positions; thecaries rateofdeciduous molars is the highest,thatofdeciduous canines is thelowest; thecaries rateof maxillary deciduous teeth is the highest for the deciduouscentral incisors,and thecaries rateof mandibular deciduous teeth is the highest for the deciduous molars.ConclusionAlthough the caries prevalence rate in deciduous teth among preschoolchildren in Hangzhou is lowerthanthenationallevel,thework ofcaries prevention andcontrol stillhasalong way to go,and the fullattention shouldbe paid bythe relevant departments to continue to strengthenoral health educationand promotion,thereby improve theoral health level of preschoolchildren.
【Keywords】 Child,preschool; Dental caries;Diagnosis,Oral
Fund program:Key Project of Medical and Health Science and Technology in Hangzhou (ZD20230076)
DOI:10.19522/j.cnki.1671-5098.2025.02.001
龋齿被世界卫生组织(WHO)认为是需重点防治的慢性非传染性疾病之一,与恶性肿瘤、心脑血管病等列为同等重要的地位。(剩余3311字)