基于Logistic回归分析构建ICU脓毒症多器官功能障碍综合征风险预测模型

打开文本图片集
A risk prediction model of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in ICU sepsis based on Logistic regression analysis
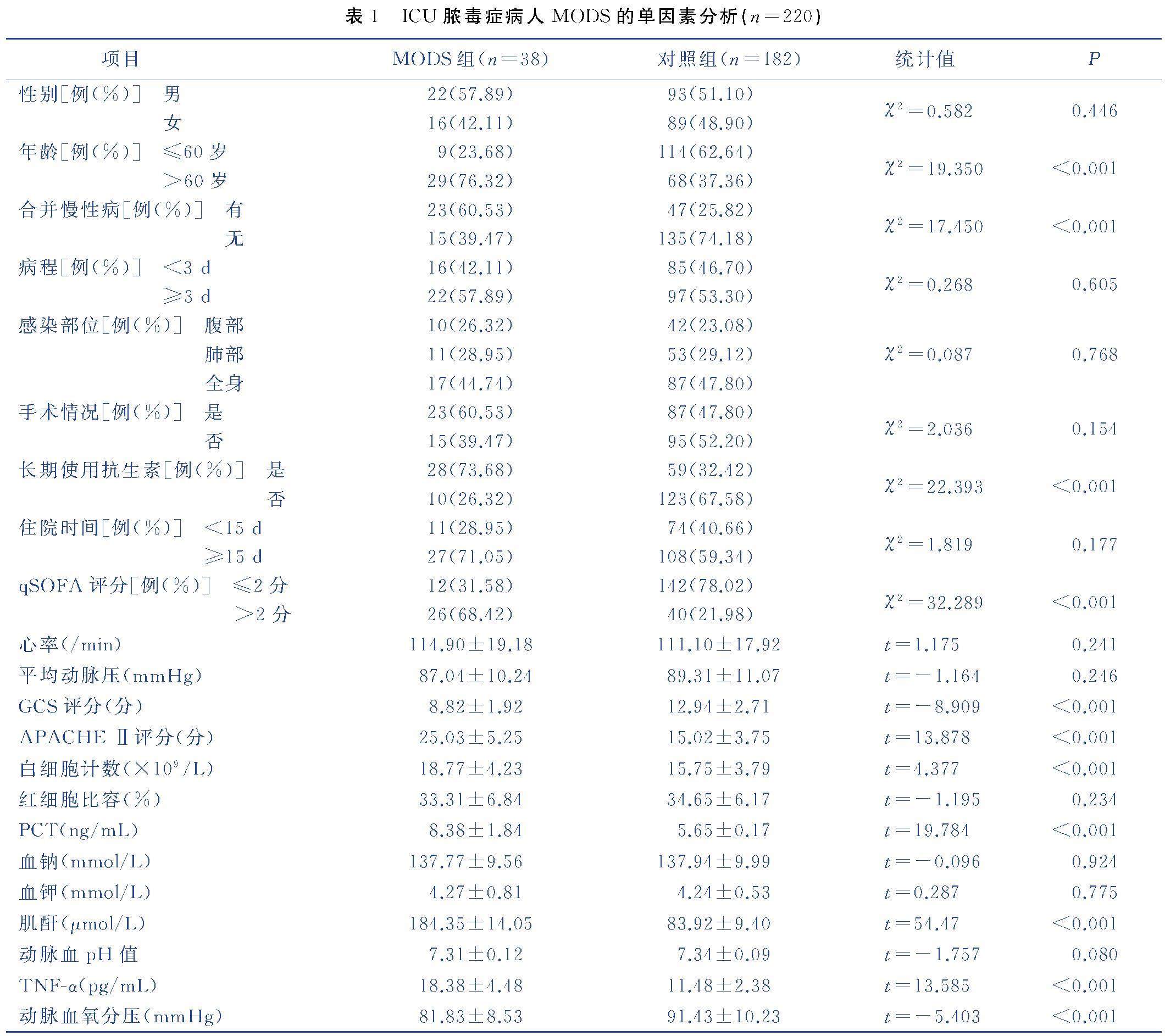
Abstract Objective:An ICU sepsis risk prediction model for multiple organ dysfunction syndrome(MODS) was constructed based on Logistic regression analysis and the effect was tested.Methods:Using the convenience sampling method to select 220 septic patients admitted to ICU from January 2020 to January 2022,who were divided into control group and MODS group according to the presence of MODS,univariate and multivariate Logistic regression analysis was used to screen independent risk factors for multiple organ dysfunction syndrome,from which the regression equation of the risk prediction model was fitted to test the effect of the model prediction.Results:38 cases with MODS.According to multivariate analysis,combined chronic diseases,qSOFA score>2,elevated APACHE Ⅱ score,PCT,creatinine and TNF-α were all independent risk factors for MODS in ICU sepsis patients(P<0.05).According to the independent predictor fitting prediction model regression equation,model Hosmer-Lemeshow test showed that χ2=4.561,P=0.683>0.05,suggesting that the prediction results were consistent with the actual situation,model ROC curve analysis showed that AUC was 0.805(95%CI 0.729-0.877),the optimal risk cut-off of 0.347,the maximum Yoden index of 0.673,corresponding sensitivity and specificity of 0.823 and 0.850 respectively,and the prediction accuracy of 85.45%.Conclusion:Based on the risk factors of MODS in ICU sepsis patients,the risk prediction model has good fit and differentiation ability,and high accuracy,which can provide an effective tool to predict the risk of MODS dysfunction syndrome in ICU sepsis patients.
Keywords sepsis;multiple organ dysfunction syndrome,MODS;risk factors;prediction model
摘要 目的:基于Logistic回归分析构建重症监护室(ICU)脓毒症多器官功能障碍综合征(MODS)风险预测模型,并进行效果检验。(剩余7814字)