基于有限元分析的固体微针力学性能研究及其集成阵列制备与表征

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:R318.08;TQ460.1 文献标志码:A
Abstract: Microneedles (MNs),as a novel transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS),offer advantages such as sustained drug delivery and minimal invasiveness, but further research is needed in material selection and mechanical performance optimization. This study employed the finite element method (FEM) based on ANSYS to simulate the mechanical behavior of conical, square pyramid,and cuboid microneedles during skin insertion, comparing the performance of materials suchas silicon,stainless steel,and resin.The results showed that conical microneedles exhibited the maximum displacement ( 5.550e-5mm )and minimum internal stress (3.315MPa) ). Under a 0.01N axial force, the conical stainless steel microneedle demonstrated strong penetration ability, with a maximum Von Mises stress of 42.104MPa A 19×19 conical microneedle array was fabricated using light-curing 3D printing, and CMC/MAL microneedles were prepared via a sequential casting method. Morphological characterization revealed uniform and smooth surfaces, with a puncture force of 0.01N/ needle,meeting skin penetration requirements. This study provides theoretical and experimental support for the design and optimization of microneedles.
Keywords: microneedles; transdermal drug delivery; finite element analysis; structural mechanics simulation
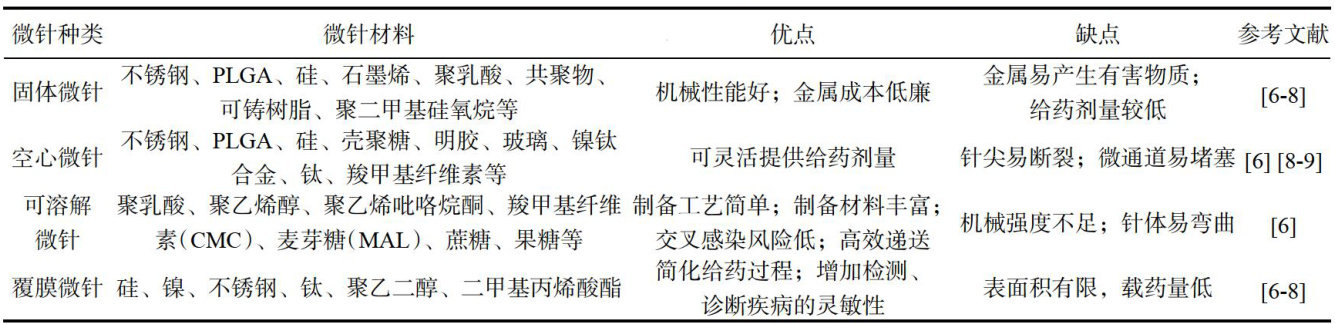
微针(microneedles,MNs)近年来因其作为经皮药物输送系统(transdermaldrugdeliverysystems,TDDS)所展现的药理学优势而受到广泛研究[1]。(剩余8871字)