后颅窝术后病人获得性吞咽障碍危险因素分析

打开文本图片集
Abstract Objective:To investigate the status quo and risk factors of acquired dysphagia in patients after posterior cranial fossa surgery,and to provide reference for early intervention of dysphagia and optimization of postoperative rehabilitation.Methods:A total of 290 patients admitted to our hospital for posterior cranial fossa surgery from January to September 2021 were selected as the research objects.The general information and related indicators of swallowing disorders were collected.Standardized Swallowing Assessment was used to evaluate patients 4 h after tracheal intubation was removed.Logistic regression analysis was used to screen the main risk factors,and ROC curve and swallowing function recovery time curve were drawn.Results:There were 113 patients had dysphagia,accounting to 38.97%.The recovery time of swallowing function was (9.49±10.06) days.Logistic regression showed that lesion size and grade of facial paralysis were risk factors of acquired dysphagia in patients after posterior cranial fossa surgery.Conclusion:The incidence of acquired dysphagia in patients after posterior cranial fossa surgery was relatively high.Lesion range and facial paralysis grade could be used to diagnose the occurrence of acquired dysphagia in patients after posterior cranial fossa surgery.Nursing staff should pay attention to the swallowing function of patients after posterior cranial fossa lesion and implement nursing intervention early.
Keywords posterior cranial fossa lesion; dysphagia; risk factors; recovery time; nursing
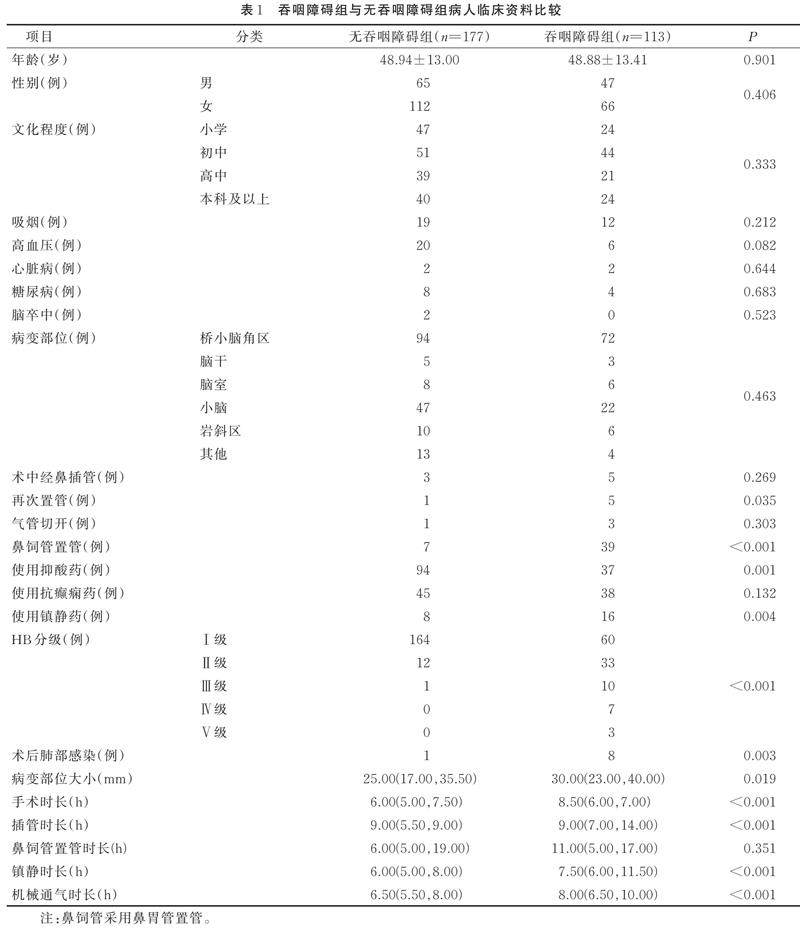
摘要 目的:调查后颅窝术后获得性吞咽障碍的发生现状及危险因素,为早期干预吞咽障碍和优化术后康复方案提供参考。(剩余10151字)