激光诱导铝等离子体结构演化及传播机制

打开文本图片集
基金项目:国家重点研发计划资助项目(No.2017YFA0304203);长江学者和创新团队发展计划资助项目(No.IRT_17R70);国家自然科学基金资助项目(No.12404467,No.12374377,No.61975103,No.627010407);国家能源石油炼制技术研发中心资助项目(RIPP,SINOPEC);山西省科技重大专项(No.201804D131036);111计划资助项目(No.D18001);山西省"1331工程"重点学科建设计划资助项目;山西省基础研究计划项目(No.202203021212122,No.202103021223210);湖北省教育厅科学研究计划项目(No.B2023162)
Abstract: A high space-time resolution imaging system with 1 ns temporal resolution and 0.01mm spatial resolution was established. The dynamic spatial distributions of neutral atoms ( AlI/ArI )and singly ionized atoms (AlII/Ar II) in plasma induced by 10GW/cm2 are measured in argon gas. The experimental results show that the plasma has an elongated morphology,and axial expansion velocity is faster than radial velocity.Due to the strong coupling between laser and argon,the shocked gas layer has a high ionization degree,and argon ions overlap with aluminum vapor plume.The morphological characteristics are consistent with the laser-supported detonation(LSD)wave.Additionally,the lifetimes of diferent species are also discussed,and the influence of upper-level energy and ion recombination on population decay rate is elucidated.This work overcomes the limitation of traditional imaging techniques,which only obtain line-of-sight integrated intensity.A novel method for observing the distribution structure of species and the expansion process. The spatiotemporal evolution of plasma is expected to provide theoretical support for the application of high-precision laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy(LIBS).
Key words: laser spectroscopy;laser-induced plasma; laser supports detonation waves; species distribu tion
1引言
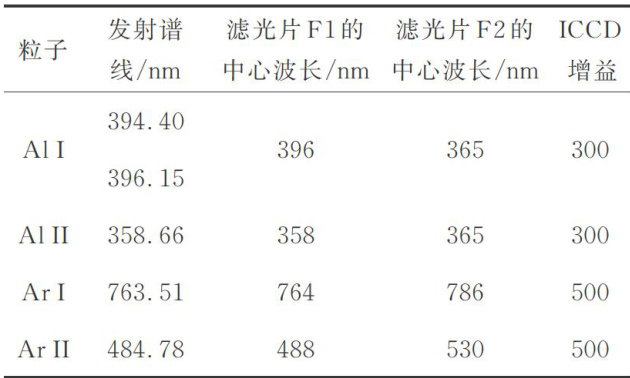
激光诱导击穿光谱(Laser-InducedBreak-downSpectroscopy,LIBS)通过分析激光诱导等离子体的发射光谱,实现元素快速检测,在工业检测领域具有重要应用[1-2]。(剩余12936字)