预测急性胰腺炎严重程度的研究进展

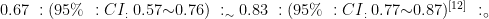
打开文本图片集
Abstract Acute pancreatitis (AP), a common acute abdominal emergency, exhibits diverse etiologies and natural disease courses. With the incidence rising steadily worldwide, a subset of AP patients may progress to severe acute pancreatitis (SAP), carrying substantial mortality risks. Therefore, early prediction of the disease severity of AP, coupled with prompt intervention, are crucial for reducing the incidence and mortality of SAP, and improving clinical outcomes. Numerous predictive approaches have been developed to assess the severity of AP, including serological parameters (C ‐ reactive protein, blood urea nitrogen, thyroid hormone, blood cell parameters, cytokines, microRNAs, etc.), imaging parameters (visceral fat area, peripancreatic necrosis volume), and scoring systems (APACHE Ⅱ , Ranson, BISAP, EPIC, CTSI and modified CTSI, JSS and new JSS scores, etc.). This article reviewed the research progress on these predictive modalities for severity of AP.
Key words Acute Pancreatitis; Severity; Serological Parameters; Imaging Parameters; Scoring Systems; Diagnosis
急性胰腺炎(acute pancreatitis, AP)是因胰酶异常激活,引起胰腺自身和周围脏器组织水肿、出血、甚至坏死的炎症反应,是一种常见的、病情进展较快的消化系统急腹症。(剩余22834字)