肠道菌群代谢物与炎症性肠病的研究进展和作用机制

打开文本图片集
Abstract The prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), a recurrent, non ‐ specific disease characterized by persistent inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, is rising globally. With the advancements in high ‐ throughput sequencing, culturomics, and metabonomics, the impact of intestinal flora and their metabolites on disease progression and host health has attracted increasing attention. This article reviewed the research progress and mechanisms of intestinal flora metabolites and IBD.
Key words Intestinal Flora Metabolites; Inflammatory Bowel Disease; Mechanisms
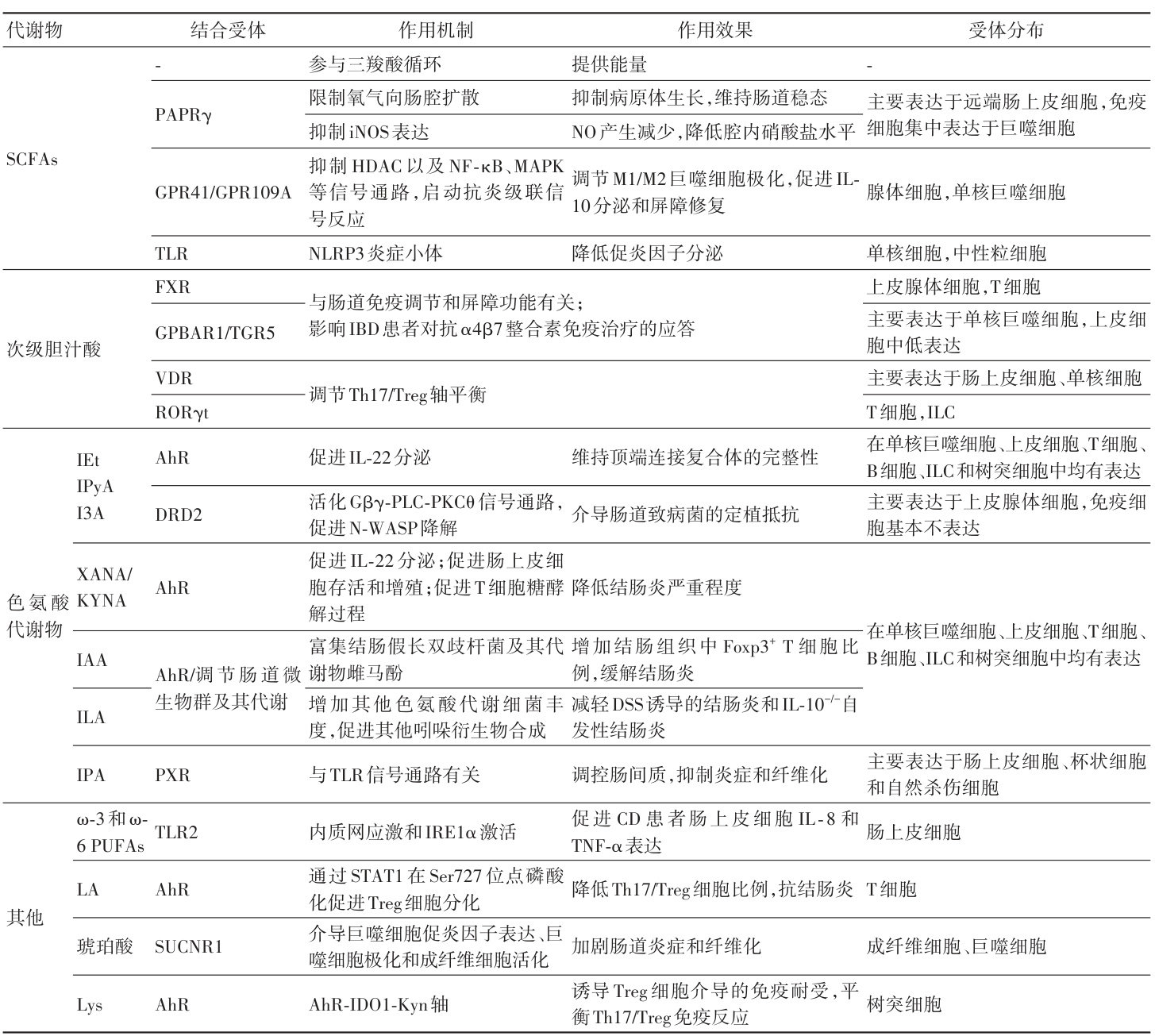
炎症性肠病(IBD)是一种复发性、非特异性、以胃肠道慢性炎症为特征的疾病,主要包括溃疡性结肠炎(UC)和克罗恩病(CD)[1]。(剩余22092字)