季铵盐阳离子聚合物对耐甲氧西林与敏感金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌选择性

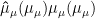
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:063 文献标志码:A
Antibacterial Selectivity of Quaternary Ammonium Cationic Polymers against Methicillin-Resistant and Susceptible s. aureus
HUANG Rui1,2,LIU Zhiguo1, ZHONG Liu1,RAO Jingyi² (1.Schoolof Science,Xihua University,Chengdu 610o39,China; 2.Schoolof ChemistryandChemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430074, China)
Abstract:Quatemnizedpoly(dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) (PQDMA)was synthesized via reversibleadditionfragmentationchaintransfer(RAFT)polymerizationandalkylationreactions.Itsantibacterialactivitybiofilmclearance capacity,hemocompatibilityandcytocompatibility weresystematically evaluated.Theresultsrevealedthat PQDMA,a quaternaryammonium cationic polymer,exhibited antibacterial selectivity distinct from the cationic antibiotic gentamicin. The minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC)of PQDMA against methicilin-resistant S.aureus (MRSA) was reduced to 16μg/mL ,aquarter of that againstwild-type S.aureus( ).PQDMA also showed stronger membrane depolarization efects and superiorpermeabilityagainst MRSA biofilms.This paradoxical selectivity may stem from MRSA's membrane structuralremodeling during resistance development,which potentially enhances the binding afinity between thecationic polymerand the bacterial membrane.Furthermore,PQDMA demonstrated excelentbiocompatibility:itsminimum concentration causing 10% hemolysis (HC10) exceeded 1024μg/mL ,and itshalf-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was 128μg/mL ,indicating favorable hemocompatibilityand cytocompatibility within its efective bactericidal range.This study offers novel insights fordeveloping cationicpolymer materials with structural targeting forantibiotic-resistantbacteria.
Key words: quaternized poly(dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate);MRSA;selective bactericidal activity;bactericidal mechanism;biocompatibility
耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(MRSA)是临床常见的耐药菌株之一,常引发术后感染,具有传播快、毒力强、耐药谱广等特点[1-5]。(剩余18178字)