烟草青枯病发生的土壤根际微环境差异

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S572.061 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1004-390X(2025)04-0176-08
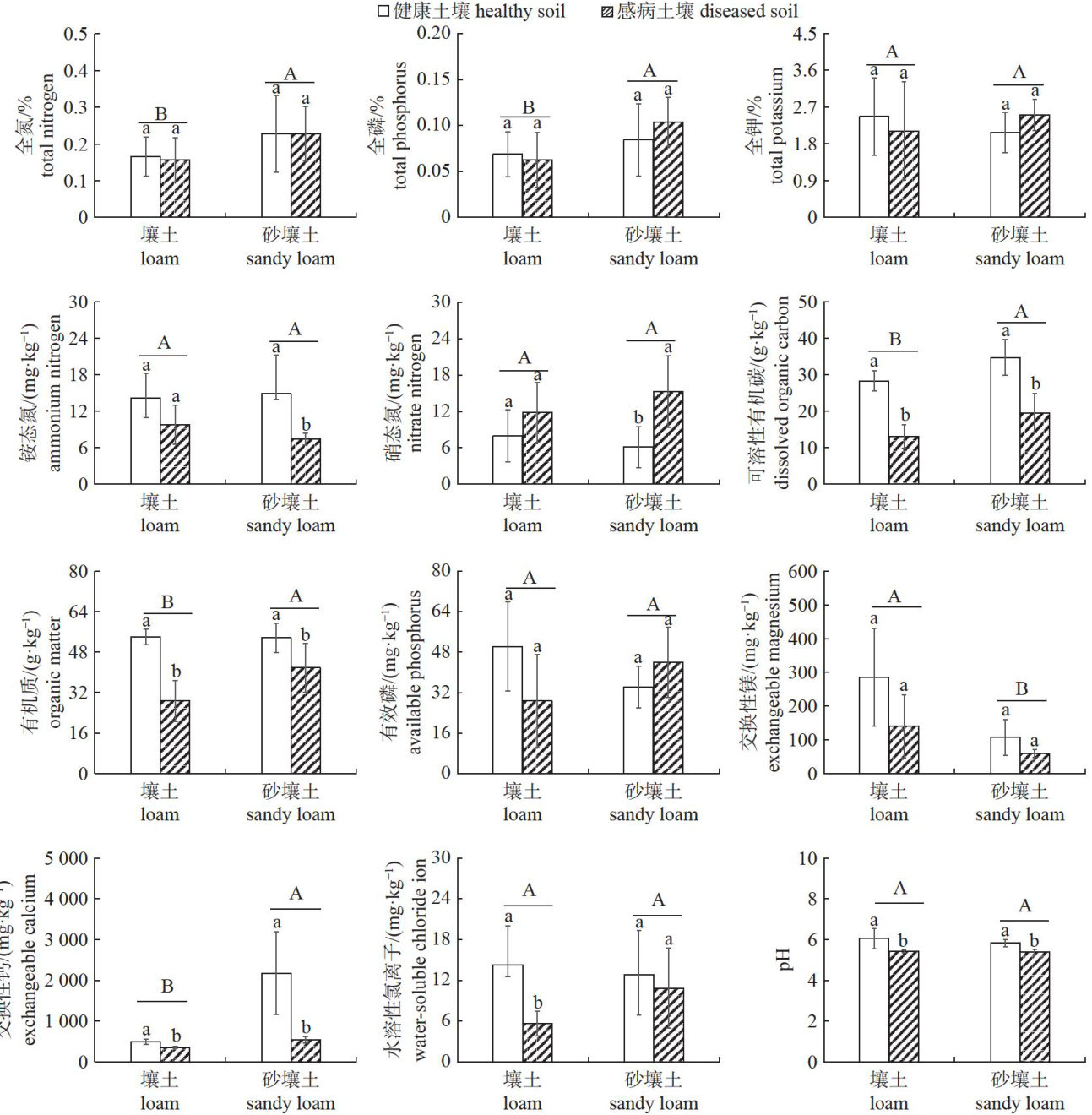
Abstract: [Purpose] To investigate the diferences of soil rhizosphere microenvironments between healthy and tobacco bacterial wilt afected plants in different soil types (loam and sandy loam) in Baoshan, Yunnan Province. [Methods] Based on field surveys and soil sampling, the nutrient content, pH value, physical properties,and biological characteristics of rhizosphere soils from both diseased and healthy tobacco plants in typical tobacco-growing areas of Baoshan were analyzed. [Results] In both soil types, the rhizosphere soil of healthy tobacco plants exhibited significantly higher levels of dissolved organic carbon, organic matter, exchangeable calcium, and pH compared to those of diseased plants. Specifically, in loam soil, these parameters were higher by 116.28% 0 87.89% 0 39.98% and 11.62% ,respectively;while in sandy loam soil, the increaseswere 77.81% , 28.20%
301.76% ,and 8.16% ,respectively. The porosity of healthy soils was significantly higher,and the bulk density was significantly lower than that of diseased soils in both soil types.Soil texture analysis indicated that coarse silt was the dominant particle fraction in both healthy and diseased soils,accounting for 29.90%-30.97% in loam and 36.18%-38.03% in sandy loam. Principal component analysis demonstrated extremely significant diffrences between healthy and diseased soil in overall characteristics, primarily atributed to variations along the first principal component (PC1). PC1 was mainly driven by indicators such as bulk density,porosity,organic matter, dissolved organic carbon, superoxide dismutase, microbial biomass nitrogen, catalase, microbial biomass carbon, ammonium nitrogen, and pH value.[Conclusion] The rhizosphere soil of healthy tobacco plants is characterized by higher porosity,organic mater content, dissolved organic carbon content, microbial biomass nitrogen, superoxide dismutase activity, catalase activity, and pH, as wellas lower bulk density and microbial biomass carbon.
Keywords: tobacco bacterial wilt; soil physicochemical properties; soil nutrient; enzyme activity
烟草青枯病是由青枯雷尔氏菌(Ralstonia so-lanacearum)引起的一种高度破坏性的土传细菌性病害[1-2]。(剩余8738字)