盐胁迫对结球甘蓝种子萌发、幼苗生长及其生理特性的影响

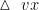
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S635.101 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1004-390X(2025)04-0092-08
Abstract: [Purpose] To explore the adaptability of seed germination and seedling growth of Brassica oleracea var.capitata L. (BOC) to salt stress, providing references for the study of growth environment of cabbage and the utilization of saline-alkali land. [Methods] The BOC was used as a test material,and the 0, 50,100,200, 250 and 300mg/L NaCl stress gradients were set up to analyze the effects of salt stress on the seed germination and seedling growth of BOC. [Results] 50mg/L ΔNaCl had no significant effect on the germination of BOC seeds and the growth of seedlings. 100- 300mg/L NaCl significantly inhibited seed germination, and the germination rate, germination potential, germination index, and vigor index all decreased with the increase of the mass concentration of saltstress,ofwhich 300mg/L salt stress led to the complete loss of seed vigor. 100-300mg/L NaCl caused a decrease in biomass, relative chlorophyll content, root vigor,but an increase in relative conductivity, malondialdehyde content, proline content, soluble sugar content, and catalase activity of BOC.[Conclusion] BOC is tolerant to low mass concentrations ( ⩽100mg/L) of salt stress, while high mass concentrations (>100mg/L) )inhibit its seed germination and seedling growth, but BOC also regulates its physiological and metabolic functions by increasing the content of osmotic regulatory substances in the body and improving the activity of antioxidant enzymes to cope with salt-stressed environments.
Keywords: Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.; salt stress; seed germination; physiological characteristics
土壤盐渍化是可溶性盐积累导致土壤性质恶化的过程,是中国最具破坏性的土地退化问题之一,已严重威胁中国农业发展,是农业部门和生态环境部门广泛关注的焦点问题。(剩余13949字)