64层冠状动脉CT血管成像技术对冠心病冠状动脉狭窄的诊断价值

打开文本图片集
Diagnostic value of 64-slicecoronary CT angiography technology for coronary artery stenosis in coronary heart diseaseShang Songtao.DepartmentofRadiology,Beihai Hospital,Xuchang,Henan
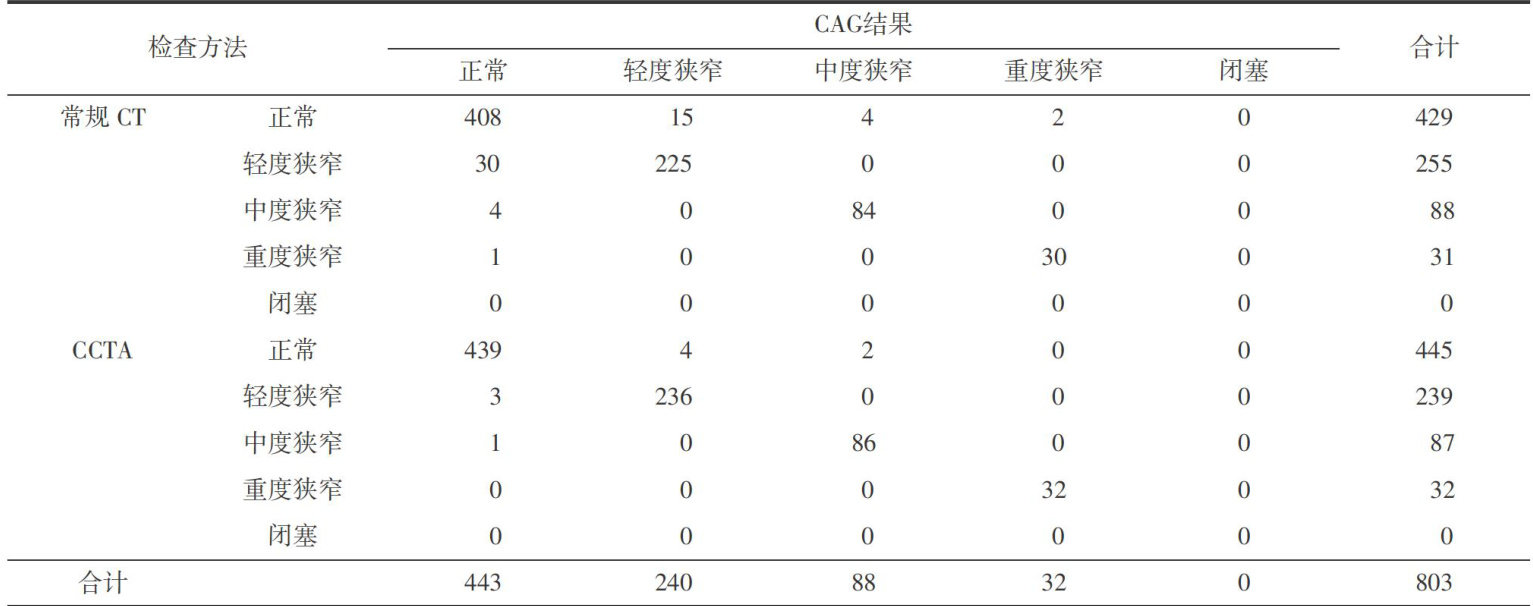
【Abstract】ObjectiveTo explore the diagnostic value of 64-slice coronary CT angiography (CCTA) technology for coronary artery stenosis incoronary heart disease.MethodsA total of12O suspected coronary heart disease patientswho visited our hospital from June 2O21 to July 2023 wereselected.Allpatients underwent routine CT, CCTA,and coronary angiography(CAG)examinations.Using the results of the CAG examination as the "gold standard"toanalyze theresults of routine CTand CCTA examinations.Compare the diagnostic value of conventional CT and CCTA incoronaryartery stenosis and calculate consistency.ResultsA total of 8O3 segmentsof coronary arteries were detected in12O suspected patients.ThroughCAG examination,itwasconfirmed that443segments were normal,240segments hadmildstenosis,88 segments hadmoderatestenosis,32segments hadsevere stenosis,andO segments wereocluded.Thesensitivity,specificityandaccuracyofCCTAindiagnosingmildcoronaryarterystenosis were higher thanthoseof conventional CTexamination,withstatistical differences (P<0.O5).There wasno statistically significant diffrence in the diagnostic valueof two types of examinations for moderateandsevere coronary artery stenosis( P> 0.05),and the consistency of CCTA in the diagnosis of coronary artery stenosis was higher than that of conventional CT scan,with statistical differences ( P <0.05).Conclusion CCTA has high clinical application value in thediagnosis of coronary artery stenosis in coronary heart disease.CCTA examinationcan clarify the degreeof coronaryartery stenosisand has strong consistency with CAGdiagnosis results.Itcanprovidereliable reference for clinical diagnosis and treatment and has high clinical promotion value.
【Key Words】Coronary heart disease;Coronary artery stenosis;64-slice coronary CTangiography;Coronary angiography;Uniformity
冠心病是临床常见的缺血性心脏病,发病率较高,因冠状动脉发生粥样硬化而导致血管狭窄或阻塞[1]。(剩余5996字)