基于FA-SVM优化LUR模型的PM2.5 时空格局模拟

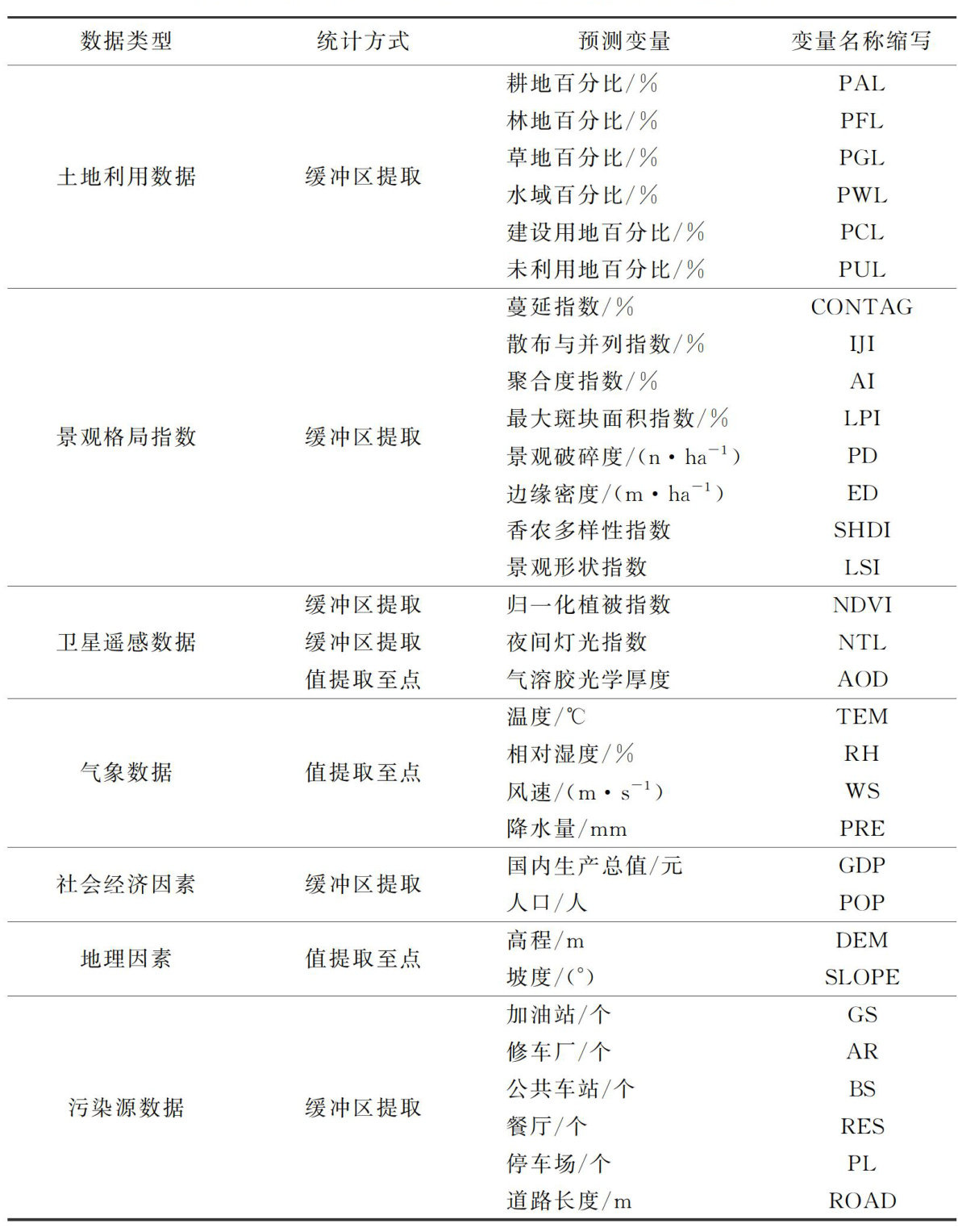
打开文本图片集
中图分类号: X513 文献标志码:A DOI:10.13338/j.issn.1674-649x.2025.03.011
Simulation of spatiotemporal patterns of PM2.5 in the Fenwei Plain based on FA-SVM optimized LUR model
Abstract To accurately capture the complex relationship between PM2.5 and predictive factors, and to obtain spatially continuous PM2.5 pollution distribution with higher resolution and prediction accuracy,a regional PM2.5 pollution early warning mechanism is constructed. In this study, the firefly algorithm-support vector machine (FA-SVM) is used to optimize the land use regression(LUR) model,estimating the PM2.5 mass concentrations in the Fenwei Plain in 2Ol9 at a spatial resolution of 1km . The results indicate that,compared to conventional LUR and SVM models,FA-SVM demonstrates superior predictive performance. The ten-fold cross-validation coefficient of determination for FA-SVM is as high as O.90,with a root mean square error and mean absolute error of 12.29μg/m3 and 8.99μg/m3 ,respectively. In contrast,the validation coeficient of determination for LUR and SVM are O.75 and O.85,respectively,with root mean square error values of 19.57μg/m3 and 14. 37μg/m3 ,and mean absolute error values of 14.84μg/m3 and 9.62μg/m3 ,respectively. PM2.5 pollution in the Fenwei Plain in 2Ol9 exhibits significant spatiotemporal heterogeneity. Temporally, PM2.5 pollution is most severe in winter,gradually decreasing in spring,autumn,and summer. Spatially,areas with relatively higher economic levels show higher PM2.5 mass concentration,forming high-value aggregation zones,while the Qinling Mountains region represents low-value aggregation zones. Overall, PM2.5 exhibits a spatial pattern of higher concentrations in the central region and lower concentrations in the surrounding areas.
Keywordsland use regression (LUR); firefly algorithm-support vector machine (FA-SVM); spatiotemporal characteristics of PM2.5 ; model optimization;the Fenwei Plain
0引言
近年来,随着经济蓬勃发展、工业化和城市化进程的急速推进,中国正面临着严峻的空气污染问题[]。(剩余17357字)