基于网络药理学和分子对接探讨桃红四物汤治疗动脉粥样硬化的作用机制

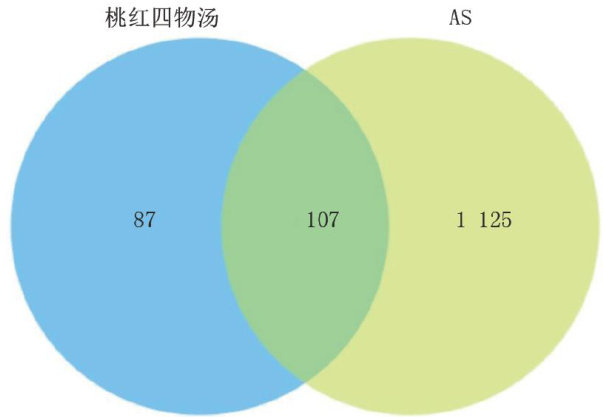
打开文本图片集
AbstractObjective:ToexplorethemechanismTaohong SiwuDecoctionforthetreatmentatherosclerosisbasedonnetwork pharmacologyandmoleculardockingtechnologyMethods:TheactiveingredientsandpotentialtargetsitesTaohongSiwuDecoction wereobtained bysearching forTCMSP.TheGeneCardsdatabasewasusedtoscreenthe lesiontargets atherosclerosis.The protein-proteininteractionnetworkdiagramsandtenetworkdiagrams"drug-activeingredient-target"and"drug-intersetio target-disease"wereestablishedbytheSTRINGdatabaseandCytoscape3.9.1stware.Theintersectiontargetswereimportedinto theDAVIDdatabaseforgeneontology(GO)functionalenrichmentanalysis,Kyoto EncyclopediaGenesandGenomes(KEGG)pathway enrichmenttopredicttheirmechanismaction.Finaly,biomoleculardockinganalysiswasperformedusingPyOLandAutoDock. Resuts:Atotalactieingredint94aedtaets32easeelatedtargtsdintersectiontagetsrdut fromTaohong Siwu Decoction.The key compounds included quercetin, β -sitosterol,kaempferol,stigmasterolandluteolin.Thekeytargets includedproteinkinaseB1AKT1)-Relreticuloendotheliosisvirusoncogeneomolog(RELA)umornecrosisfactor)tur proteinp53(53),mitogen-activatedproteiinase(PK1),itogenactivatedproteininase(APK14)andintelekin66) estrogen receptor1(ESR1),catenin β,(CTNNB1),retinol x receptor α (RXRA).A total 1 836 GO itemswere obtained through GO bioprocessencntalysisding6icalpross)6laropots(C)nd33olelarct).
Atotal163KEGGmetabolicpathwayswereenriched.ThemoleculardockingresultsshowedthatthecorecompoundTaohongSiwu DecoctionshowedbeterbindingeficacywithAKT1andTNFproteins.Conclusion:Taohong Siwu Decoctionmightactoncoretargets suchasAKT1,I6andFthoughitsoecomponents,idingquercetinandaempferolthrebegulatingsignalingpathyuch asadvanedglycatiodprodctsandtheieceptors(AGERAGE)anusinase(JAK)sinaltransducerandactivatortart (STAT),andposphatidylioiol3-iase(P3KproteininseBKtomodulatebgicalproesessuchasinfammatoryse immune response,response toreactive oxygen species,andapoptosis,toexerttherapeuticefectsonatherosclerosis. Keywordsatherosclerosis;Taohong Siwu Decoction; network pharmacology;molecular docking;mechanism
动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,AS)是一种在血管壁发生的长期慢性炎性病变,其特征表现为脂质的沉淀和免疫细胞的浸润,主要发生在大中型血管壁上,由动脉最内层的斑块积聚导致动脉壁增厚和硬化,进而引起动脉管腔狭窄,常作为冠心病、外周动脉病变和脑血管疾病的伴随疾病[1-3]。(剩余13256字)