学龄前儿童基本动作技能与学习品质的关系研究

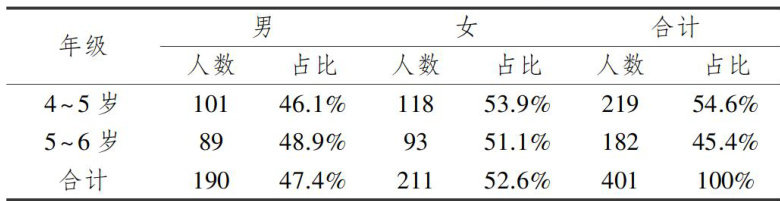
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:G804.22 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1009-9840(2025)03-0050-07
Abstract: To clarify the relationship between Fundamental Movement Skills (FMS) and learning quality in preschool children, a cluster sampling method was used to conduct on-site assessments of 449 preschoolers. Statistical analyses, including independent samples t-tests, Pearson partial correlation analysis, and multilevel linear regression models, were conducted. The results indicated that both FMS and learning quality improved with age( P<0.001 ),while no significant gender differences were observed( P>0.05) . The development of learning quality was unbalanced across its dimensions: learning attitude improved the fastest, followed by competence motivation, while attention/persistence developed more slowly. Correlation analysis revealed significant associations between FMS and learning quality ( R=-0.132 to -0.424,P< 0.001),with locomotor FMS showing the strongest correlation ( R=-0.424 , P<0.001 ), followed by object control FMS ( R=-0.262,P<0.001) ,and stability FMS showing the weakest correlation ( R=-0.132 , P<0.001 ) . Regression analysis further demonstrated that bilateral symmetrical locomotor FMS had the strongest predictive efect on learning quality ( B=-0.079 , P<0.001 ),followed by unilateral fine object control FMS ( B=-0.034 , P< 0.001 ). Asymmetrical static stability FMS significantly predicted attention/persistence only( B=-0.002 , P<0.001 ). Overall, the FMS that significantly predicted learning quality were generally characterized by high levels of coordination, control, repeatability, coherence,and continuity, whereas those relying primarily on speed or dynamic output had weaker predictive effects.
Key words: fundamental movement skills; learning quality; preschool children; motor coordination
学习品质是确保儿童做好人学准备最为关键的问题之一,对其未来的学业成就和终身发展具有深远影响[1]。(剩余14111字)