灌丛人侵对黄河三角洲湿地土壤粒径空间异质性特征的影响研究

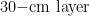
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S153.6:Q948 文献标识号:A 文章编号:1001-4942(2025)06-0111-10
AbstractGlobal changes and human activities induce great shrub encroachments in coastal wetland ecosystems,altering their structures and functions.Taking the typical shrub-encroached wetland in the Yellow River Delta as a case and based on the GIS platform,we quantified the spatial pattern heterogeneity of soil particle composition ( 0~80cm, )by lacunarity analysis and analyzed the effects of different shrub encroachment types on soil particles by the cold(hot)spot analysis.The results were as folows.(1) The contents of different size soil particles in shrub-encroached wetland showed as silt > sand > clay. The content of clay and silt increased with the increase of soil layer depth while that of sand decreased.(2)The lacunarityof clay was higher than that of silt and sand in 0~20 -cm layer,and they were similar in 20~30 -cm layer. But below ,the lacunarity of clay decreased gradually utill lower than that of silt and sand.(3) The hot-spot area of sand in 0~50 -cm layer occupied the largest in shrub patches,while that of clay in 0~40 -cm layer and silt in 0~50 -cm layer (except 1O\~2O-cm layer)occupied the largest in tidal flat without shrubs.The hot-spot areas of soils in Tamarix chinensis cluster patches and bare land were moderated.These results could provide scientific references for accurate assessment of wetland shrub-encroached efect and wetland protection and res
toration.
KeywordsWetland shrub encroachment; Soil particle size; Spatial heterogeneity;Lacunarity analysis;Cold-hot spot analysis; Yellow River Delta
由于全球气候变化和人类活动,天然草本生态系统逐渐被灌木等木本植物侵占,即发生灌丛化现象[1-2]。(剩余12091字)