基于机器学习的楣石微量元素特征判别岩浆岩类型

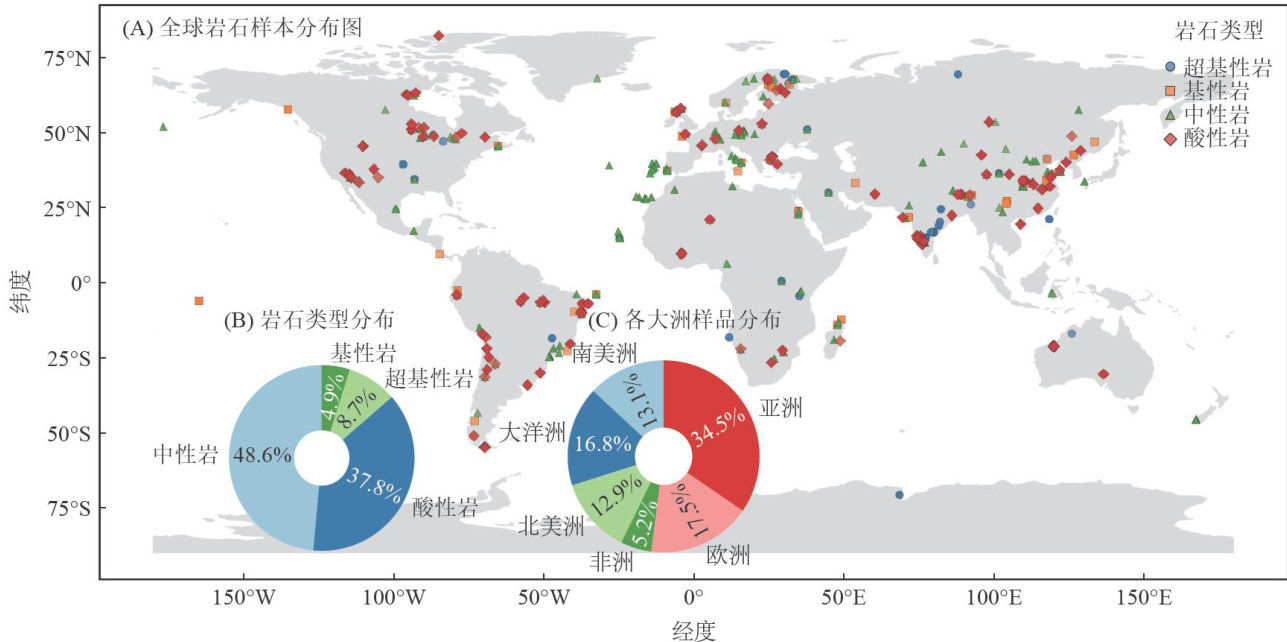
打开文本图片集
Abstract: Titanite,asanaccessory mineral inigneous rocks,provides a record of the evolution of geochemical environments during magma diferentiation,and its trace element characteristics hold significantpotential inrock type identification. Although binary discrimination plots have been applied in traditional clasifications of igneous rocks based on titanite trace element content, their limitations in clasifying complex rock types have become increasingly evident.In recent years,with the accumulation of geological data and the development of machine-learming technologies,data-driven geological research methods have been widely applied.This studyutilized publicly available titanite trace element data and employed genetic programming symbolic regression to construct a mathematical expression for discriminating igneous rock type.By applying four machine-learning algorithms (support vector machine,k-nearest neighbors,XGBoost,and random forest),a classificationmodel for igneous rock type was constructed,whichaccuratelydistingushesultramafic,mafic,intermediate,and felsicrocks.SHAPanalysisrevealed significantassociations between titanitetrace element compositions and igneous rock types,indicating thattitanite geochemistry can serve as an effective indicator for lithological classification.
Key words:titanite;trace elements;igneous rocks;genetic programming symbolic regression;machine learning
在岩桨岩微量元素地球化学研究中,受限于岩浆侵位过程中的同化混染、后期的热液蚀变以及构造变形的影响,全岩地球化学往往呈现出复杂的微量元素组成特征(Hammoudaetal.,1996;Tommasini and Davies,1997; Daviesand Tommasini2000; Knesel and Davidson, 2002; McLeod et al.,2012;赵令浩等,2020)。(剩余21505字)