基于空间随机森林的矿产资源定量预测
——以河北大庙—红石碰钒钛磁铁矿带为例

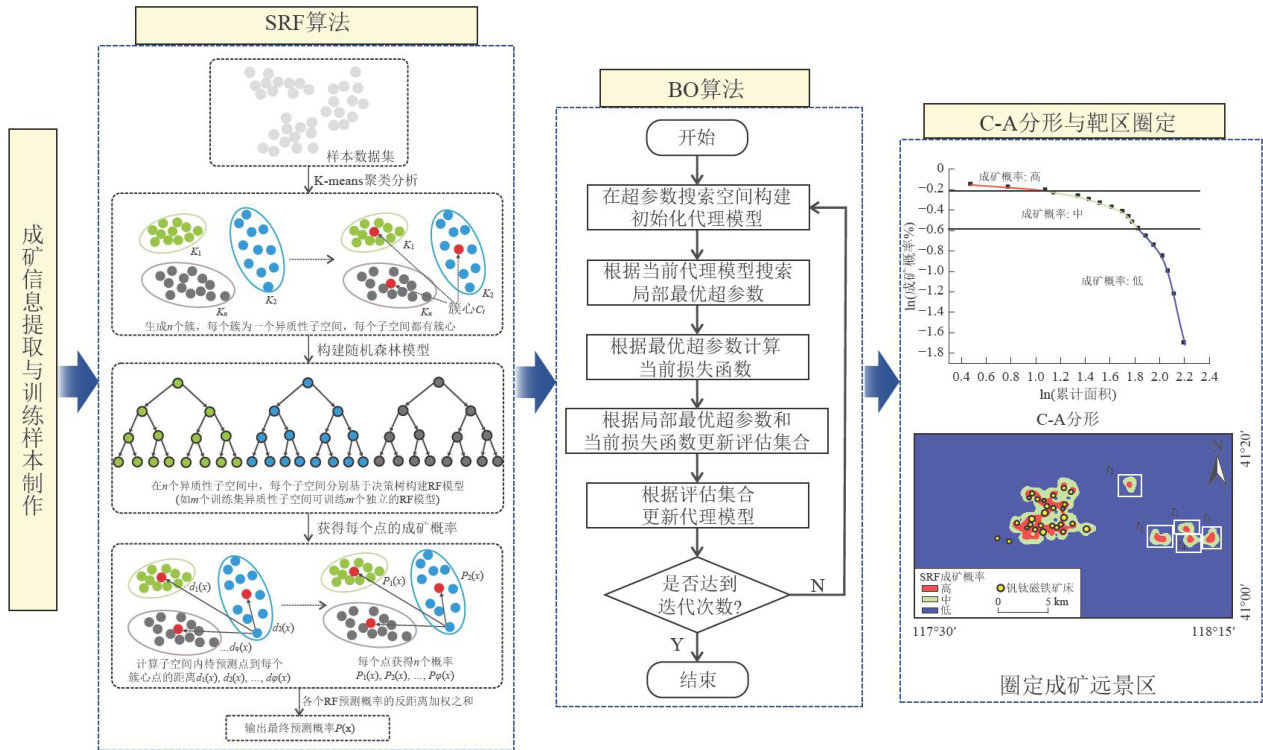
打开文本图片集
Abstract: Existing mineral prospectivity mapping (MPM) methods pay insuficient atention to spatial heterogeneity and spatial autocorrelation, which limits their effectivenessTo address this,we have developed aspatialrandom forest (SRF)method that integrates K-means clustering with traditional random forest (RF) for MPM in the Damiao-HongshilaFe-V-Tiore belt,Hebei Province,China.The SRF methodfirstconstructs spatiallyheterogeneous subsets via K-means clustering, establishing heterogeneous RF models as base learners.The predicted probabilities are subsequently aggregated using inverse distance weighting according to the distances between the target center locations and the corresponding cluster centroids. Our method outperforms traditional RF,with an improved area under the curve score of 6.83% ,an improved accuracy of 8.62% ,and an improved F1 score of 8.52% while maintaining high interpretability. Based on the SRF model and a concentration-area fractal analysis,five prospective targets weredelineated for mineral exploration in the studyarea.In summary,SRF provides an effective framework for modeling both spatial heterogeneity and spatial autocorrelation in MPM.
KeyWords:spatialrandom forest;Bayesian optimization;concentration-area fractal analysis;Damiao-Hongshila Fe-V-Ti ore belt;mineral prospectivity mapping
矿产资源定量预测是实现找矿突破的重要手段。(剩余22921字)