面向自主水下机器人的深海污染物检测

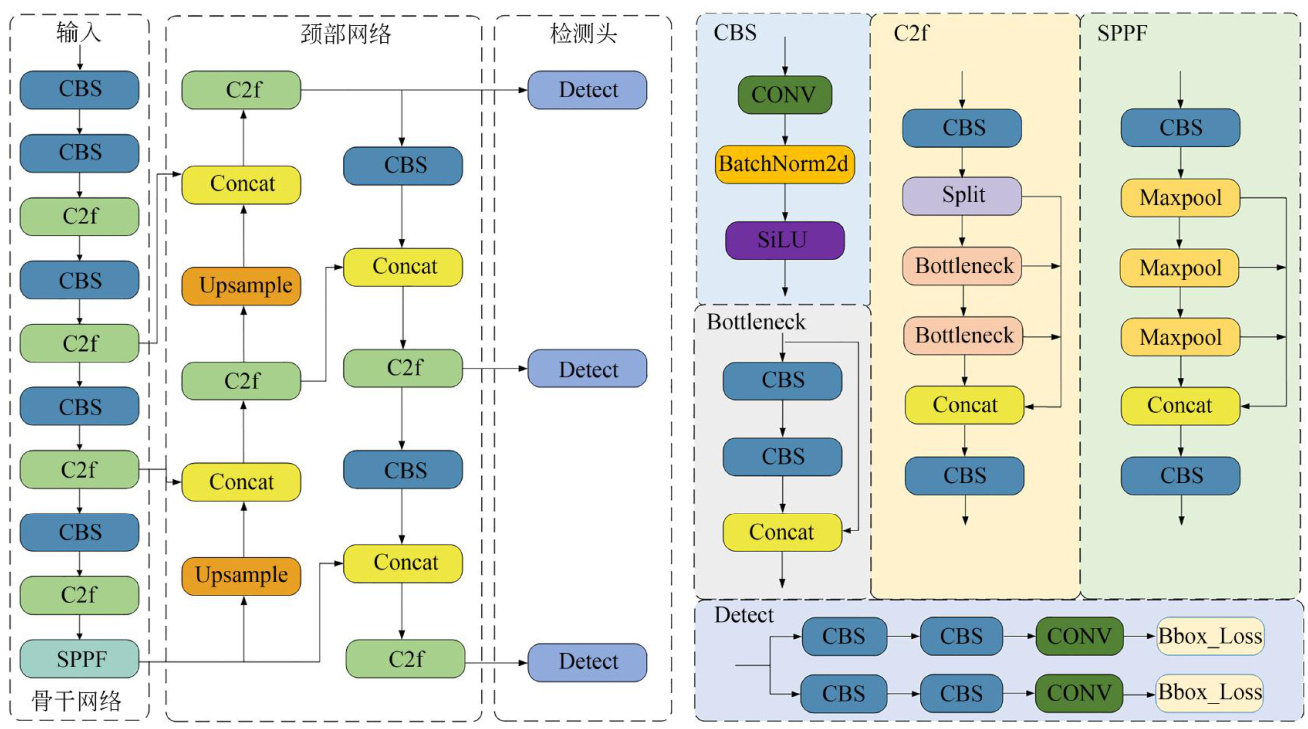
打开文本图片集
Deep-sea pollutant detection for autonomous underwater robots
ZHANG Biao*, ZHU Zhenyang,XU Jiazhong (Heilongjiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Complex Intelligent System and Integration, Harbin University ofScience and Technology,Harbin15oo8O,China) * Corresponding author,E-mail: zhangbiao@hrbust. edu. cn.
Abstract:Marine debris constitutes a significant global environmental challenge.Autonomous underwater robots offer a potential solution for the removal ofdeep-sea debris.To enable rapid and accurate detection of such debris,this study presents a lightweight detection model,termed Deep-sea Debris YOLO (DebrisYOLO),developed using deep learning techniques. An initial deep-sea debris dataset was constructed based on the Deep-sea Debris Database provided by the Global Oceanographic Data Centre (GODAC). Subsequently,an enhanced BiFPN feature fusion network was employed to reduce model parameters while enhancing background discrimination capabilities. A lightweight detection head was designed to decrease computational complexity,thereby improving the model’ s practicality and deployability for deepsea debris detection.Furthermore,the Wise-DIoU(Wise Distance Intersection over Union) loss function was introduced to mitigate the influence of low-quality samples,enabling more precise localization of deepsea debris.Data augmentation and adaptive color-balanced underwater restoration were applied to enrich the training dataset.Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed Debris-YOLO model achieves improvements of 1.3% and 1.6% in mAP0.5 and mAP0.5:0.95 , respectively, compared to YOLOv8n,while reducing the number of parameters and GFLOPS by 48.2% and 36% ,respectively. Key words: computer vision; target detection;underwater robot;deep-sea debris
1引言
海洋垃圾的累积对海洋生态构成了相当大的威胁,已经成为了全球性的问题[1-2]。(剩余18127字)