空间碰撞碎片云探测识别与快速编目能力评估

打开文本图片集
Evaluation of detection, identification and rapid cataloging capabilities for space debris cloud
Abstract: Advancements in space-ground integrated surveillance techniques have expanded detection coverage and reduced object revisit times,enabling the colection of multiple orbit tractlets of new debris within hours of an event and thereby facilitating timely tracking and cataloging.This study evaluates the detection and cataloging capabilities for monitoring debris clouds using space-based optical systems. Utilizing historical two-line element data,the identification and cataloging potential of debris generated by the COS
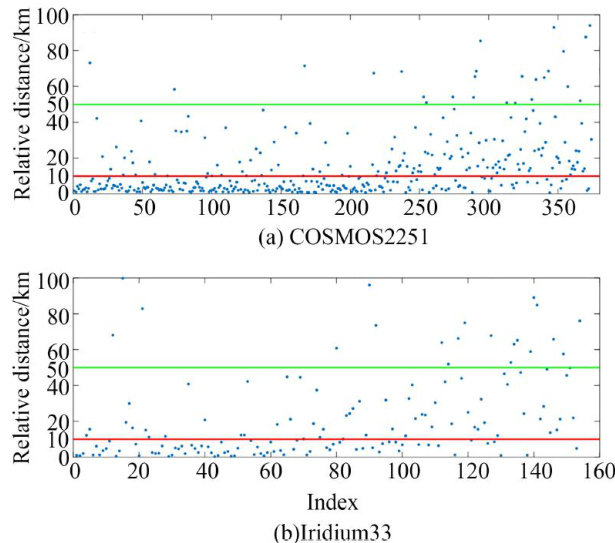
MOS-2251/Iridium-33 satelite collision were analyzed,assuming a space-based optical detection constellation of 24 satellites. Results indicate that 99% ofnew debris fragments can be resolved within 20min. 1 utes post-colision.Analysis of randomly selected samples of 1OO debris fragments from each satelite revealed that 81% of COSMOS-2251 debris and 87% of Iridium-33 debris possess at least 1O observable tractlets within one day following the collsion.Considering all observable tractlets within this timeframe, 70% of COSMOS-2251 debris and 73% of Iridium-33 debris were successfully cataloged. These findings demonstrate that a well-designed space-based optical surveillance system can catalog over 70% of new debris resulting from space collisions within one day.
Key words: space collision;debris cloud;object detection; orbital catalogue; space-based space surveil-lance
1引言
随着人类航天活动的日益频繁,空间碎片数量快速增长。(剩余14096字)