基于遥感监测的黑泥湾筏式海带养殖区时空变化研究

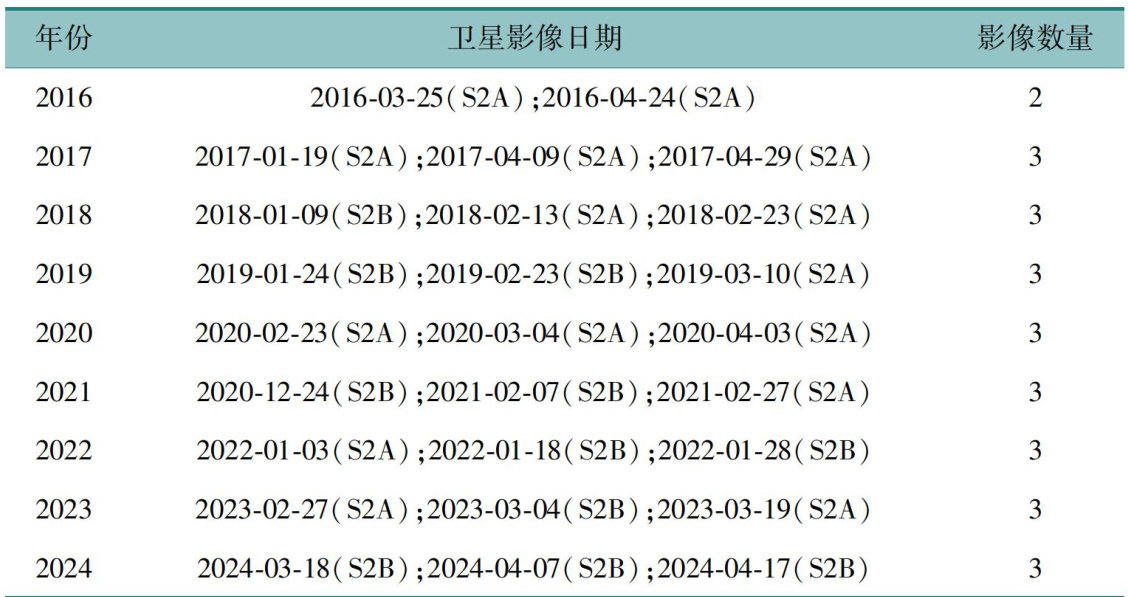
打开文本图片集
(1.Schoolof InformationEngineering,ZhejangOcean UniversityZhoushan316022,China;2.State KeyLaboratoryfSatelite Ocean Environment Dynamics,Second Institute of Oceanography,Ministryof Natural Resources,Hangzhou 310ol2,China;
3.Institute of Marine Instrumentation,Qilu Universityof Technology(Shandong Academy ofSciences),Qingdao 26061, China;4.Shandong Provincial Academician Workstation,Shandong Academy of Sciences, Jinan 250o14,China;
5.Laoshan Laboratory,Qingdao 266237,China)
Abstract:Accurate assessment of the scaleanddistribution of offshore marineaquaculture iscritical for effective management,spatial planning,andecological protection.Thisstudyemployed high-resolutionSentinel-2A/Batellite imagery,a U-Netdeeplearningmodelforautomaticfeatureextraction,andhuman-computerinteractivecorrctiontomap the spatialextent of raft-based kelpfarming in Heiniwan Bay from2016 to2024.Theanalysisrevealedathree-phase development trajectoryintheaquaculture areaover thenine-yearperiod.Spatialdistribution exhibitedastable“north-south agglomerationwith central sparsity”patern.The observed spatiotemporal dynamics reflectthe combined influence of technolgical advancements,policy interventions,andnatural environmental conditions.These findings oferarobust scientific basis foroptimizingaquaculture zoning,adaptive management strategies,and ecological governance in coastal regions with comparable aquaculture practices and environmental settings.
Key Words : Sentinel-2A/2B;remote sensing;raft-based kelpaquaculture;deeplearning; Heiniwan Bay;spatiotempora evolution
海水养殖是全球水产行业的重要组成部分,其作为现代农业与渔业的结合模式,既能够满足人们日益增长的海产品需求,又能有效促进沿海地区的发展[1]。(剩余11038字)