小麦赤霉病重发原因分析及 “1+2” 药剂防控模式探索

打开文本图片集
中图分类号 S435.121.4 文献标识码A 文章编号 1007-7731(2025)15-0067-03
DOI号 10.16377/j.cnki.issn1007-7731.2025.15.017
Analysisofthereasonsfor thesevereoutbreakofwheat scaband explorationof the Π64Π1+23 pesticide control model
YANGXuewen
(Chaohu City Agricultural Technology Extension Center, Chaohu 238OOo, China)
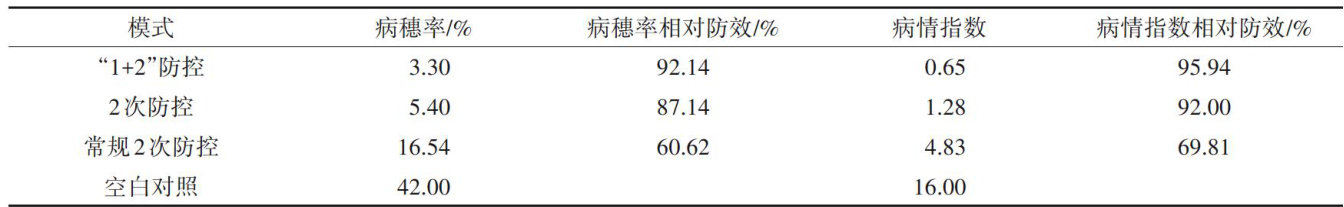
AbstractBased on the occurrence of wheat scab in Chaohu,Anhui,in 2O24,an analysis was conducted on the causesof its severe outbreak.Additionally,a“ 1+2,, chemical control demonstration was carried out in affected wheat fields,and its efectiveness was summarized.In 2O24,wheat scab in the study area was characterized by early maturation of ascocarps on ricestubbles,a high pathogen carrier rate,and severe field disease severity.The main reasons forthe severeoutbreak of wheatscab inthe studyarea were identified asabundant pathogen sources,favorable weather conditions from April to May (daily average temperature >15∘C ,more than 11 days with precipitation >0.1 mm),weakresistance (ortolerance)ofwheat varieties,andthedevelopmentof fungicideresistanceinthescab pathogens.The“1+2”chemicalcontrol model involvedanadditionalthirdapplication (during the wheatboting stage in mid-to-late March,combined with the control of sharp eyespot)onthebasis of the conventional twoapplications (the firstatthe initial wheat flowering stageandthe second7-1O days later).Theexperimental resultsshowed that the relative control eficacyof diseased panicle rate and disease indexof wheat scab by the“1+2"chemical control model was 92.14% and 95.94% ,respectively,demonstrating good prevention effects. This study provides a reference for selecting an appropriate chemical control strategy for wheat scab.
Keywordswheat scab; fungicide resistance;pesticide control; disease index
赤霉病是对小麦生产影响较大的真菌性病害之一,由多种镰刀菌引起,在淮河以南及长江中下游麦区发生较为严重。(剩余3287字)