小檗碱调节肠黏膜免疫屏障功能以防治脓毒症的机制研究进展

打开文本图片集
关键词:小檗碱;黄连素;脓毒症;肠黏膜免疫屏障;免疫紊乱;Notch信号;综述中图分类号:R259.153 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1007-3213(2025)08-2076-07DOI:10.13359/j. cnki.gzxbtcm.2025.08.037
Abstract:Sepsis isa systemic inflammatory response syndrome triggered by infection,and the abnormal inflammatoryresponse leads to the damageof intestinal mucosal barrier.The intestinal mucosal barrierconsistsof four parts,namely biological barrier,chemicalbarrier,mechanical barrier,and immune barrier.The injured intestinal mucosal barrier is considered as the“initiating organ”of multiple organ dysfunctions in sepsis,with the immune barrier being particularly critical to the progression of sepsis.Berberine(also known as berberine hydrochloride) is an active alkaloid extracted from Berberaceae plants such as Coptidis Rhizoma,and possesses multiplepharmacological actions includingantibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.It has been widely used in the treatment of various diseases,including diarhea and arrhythmias.This articlereviewed the progressin recent research on the protective efects and mechanism of Berberine against sepsis-induced intestinal mucosal immune barrier damage.The recent studies have shown that berberine can modulate intestinal mucosal immune function in sepsis via regulating the TLRs signaling pathway,Notch signaling pathway,and dendritic cell(DC)function,by inducing feroptosisof macrophages in intestinal mucosa,and byregulating the imbalance of gut microbiota in sepsis patients.The unique advantages of berberine and its promising application prospects in the treatment of sepsis have been demonstratedby itseffectson protecting and repairing the intestinal mucosal barrier and on improvig the sepsis-induced intestinal mucosal barrier damage.The in-depth research into its therapeutic mechanisms and the exploration of optimized strategies for using berberine to preventand treat sepsis-induced intestinal mucosal barierdamage areof great significance for enhancing clinicaloutcomes insepsis treatment,and will provide new insights and directions for the prevention and treatment of sepsis.
Keywords:berberine;berberine hydrochloride; sepsis;intestinal mucosal immune barrier; immunedysfunction;Notch signaling;review
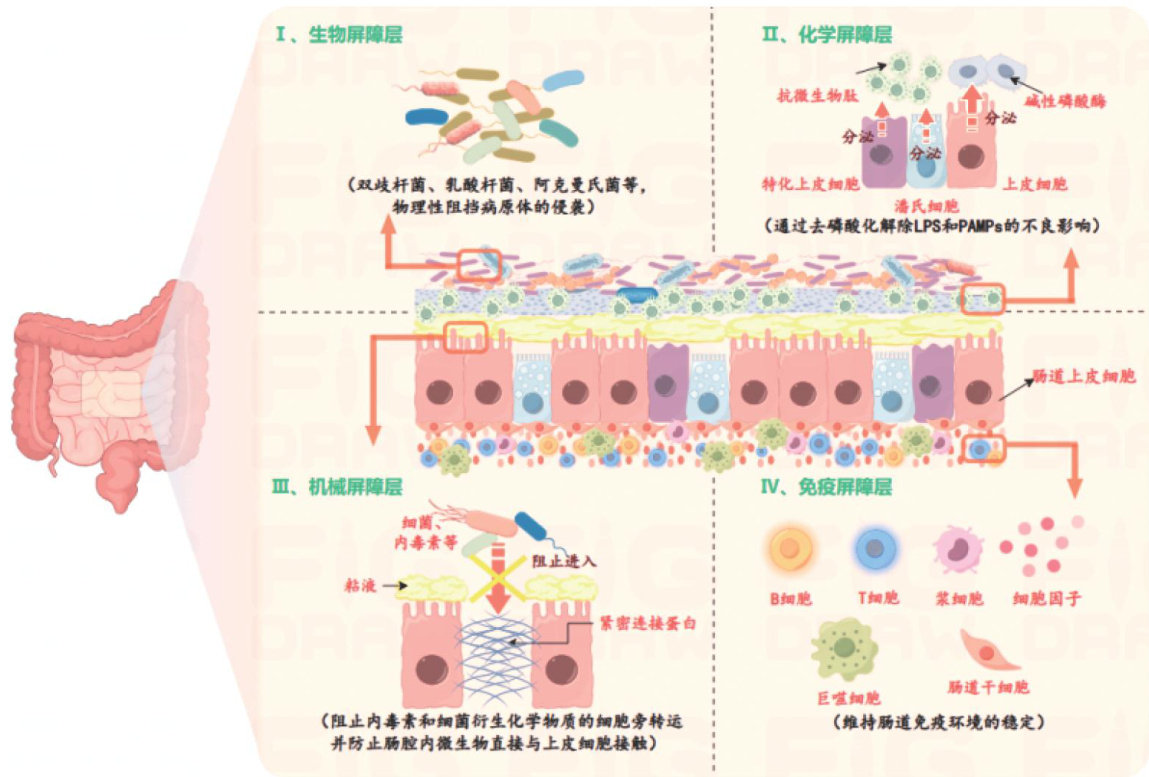
脓毒症是机体对感染反应失调导致的危及生命的器官功能障碍,已成为全球重症监护室常见致死原因之一。(剩余13478字)