陆地棉gag基因家族的鉴定与分析
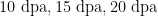
打开文本图片集
Abstract:[Objective]Transposableelementsareamajordriverof genomeevolution,yetthefunctionsofthegaggenefamilyin uplandcotonremainunclear.Thisstudyaimedtoidentifymembersofthegaggenefamilyinuplandcotonandanalyze their structuralcharacteristics,evolutionaryelationshipsandexpresionpates toexploretheirpotentialolesinottongrowth, development,andstressresponses.[Methods]BasedontheTM-1reference genomeofuplandcotton,gaggenefamilyembers were identified using HMMER software,NCBI-CDDdatabaseandthePfamdatabase.Bioinformaticstoolswereemployed to analyze theirphysicochemical properties,subcellularlocalization,andchromosomaldistribution.Phylogenetictrees were constructed using ClustalXand MEGA X.Cis-acting elements in promoter regions were predicted using PlantCARE website, andLTRtransposon distribution wasanalyzed with RepeatMaskerandLTR_retriever.Transcriptomedata and quantiative real-time polymerase chainreaction were performedtoanalysis theexpressionpaterns and functionsof gag genes.[Results]A total of 166gag genes was identified in uplandcoton with significantly more genes inthe A sub-genome than in the D sub-genome.Phylogeneticanalysisdividedthefamilyintotwomajorsubfamilies(ninesubgroups)withdiversegenestructures, mostofwhich are located inLTR transposons.Promoter analysis revealed abundant cis-acting elements relatedtocoton growth,development,hormoneresponses,and stressadaptation.Expresionprofilingshowedthatcertaingenes,suchas
Ghir_A09Go13490and Ghir_D04G004460,werehighly expressed inspecifictisses(e.g.,ovules,fibers)orunderstre conditions(e.g,hightemperature,saltstress).Conclusion]hegaggenefamilyexhibitssignificantdiversityinuplandcotton with its evolutionclosely linkedtoLTRtransposonactivity.Somemembersmayplayroles inabioticstressresponsesandseed development, offering potential targets for cotton genetic improvement.
Keywords: Gossypium hirsutum L.; gag gene; bioinformatics; expression pattern
转座子活动是生物基因组进化的重要驱动力,转座子不均等扩增调控同源基因转录、剪接和翻译,进而影响棉种谱系的特异分化。(剩余12934字)