GhALMT10在干旱胁迫下的功能鉴定

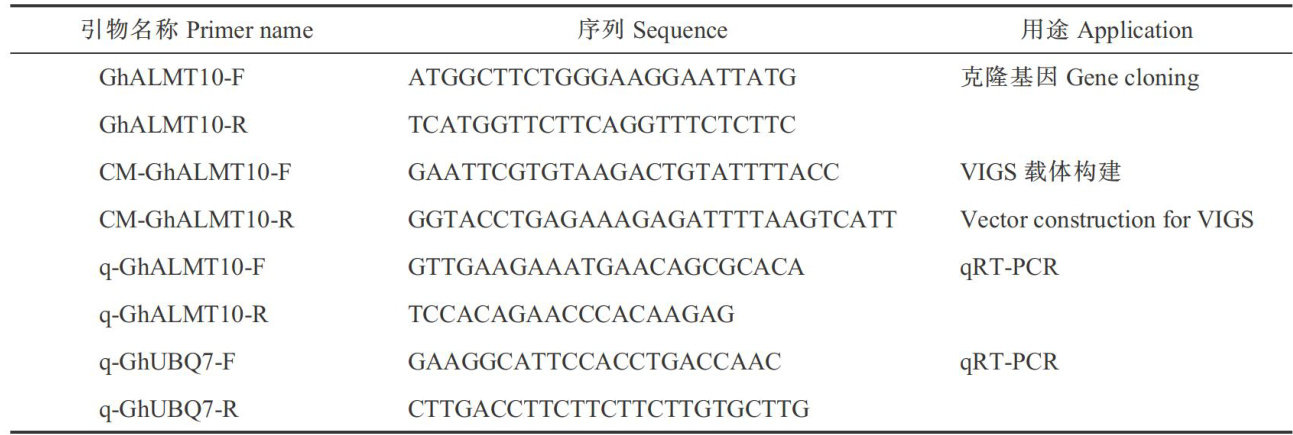
打开文本图片集
Abstract:[Objective]Thisstudyaimedtoexplorethebiologicalfunctionsofoneof thealuminum-activatedmalate transporter (ALMT)familygenes,GhALMT10,inthedroughtresistanceofcoton,therebyestablishingafoundation foradeeper understandingof themechanisms ofdroughtresistance incoton.[Methods]ThecodingsequenceofGhALMT10 gene was amplifiedfromGossypiumhirsutumTM-1bypolymerasechainreaction (PCR),followedbybioinformaticsanalysis.The expresionpattensofthisgneinvariouscotontissuesaswellasunderdroughtstress,wereassessedusingquantitative real-timePCR(qRT-PCR).Aditionally,thebiological functionof thisgeneincoton'sresponsetodrought stress was preliminarilyverifiedusingvirus-induced gene silencing(VIGS)technology.[Results]Thecodingregionof GhALMT0spans 1 401bp,encoding aproteincomposed of 466aminoacid residues,which is predicted to be stableand hydrophobic. Phylogeneticanalysisindicated that GhALMT10 iscloselyrelatedto GrALMT10,GaALMT10-like,HsALMT10,and TcALMT10.Results byqRT-PCR indicated thatGhALMT10is expressed incotonroots,stems,and leaves,withthe highest expresion levelobservedin theroots.Comparedwiththecontroltreatment withclear water,theexpresionlevelofGhALMT10 was low at 3h of drought sress,and then significantly increased at 6n and9h of drought stress treatment,while it significantly decreased at 24h Furthermore,thesurvival rateofGhALMT10-silenced cotton plants was significantly higher under drought stresscomparedwith thenegativecontrolplants.Thewaterlossrateof detached leaveswassignificantlyreduced,the chloropyll content in leavesafterdroughttreatmentwas significantly increased,and themalondialdehydecontentwas significantlydecreased inGhALMT10-silencedcoton plants.[Conclusion]Thedrought toleranceof GhALMT10-silenced plants Was significantlyenhanced,indicating that GhALMT10gene negativelyregulates droughtresistance incotton.
Keywords:cotton;GhALMO;drought stress;expressonpaternanalysis;virus-inducedgenesilencing;physiologcaland biochemical indicators
棉花是我国重要的经济作物。(剩余18408字)