沙眼衣原体感染对人乳头瘤病毒相关宫颈癌进程机制的影响研究

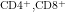
打开文本图片集
Effct Chlamydia Trachomatis on progress the HPV-related cervical cancer Lu Liquan, Zhang Xiaoxue, ZhangAi,Lyu Yingying.“ , , ,
【Abstract】 ObjectiveTo explore the effect Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) on human papillomavirus (HPV)persistence and how CT facilitatesthe progress cervical cancer.MethodsThirty-two CT/HPV coinfections,48HPVinfections,30CTinfections,and20 healthyindividualswerecollcted.Langerhanscell(LC) functionwas detected byantigen-presentingabilityanalysis.Immunluorescence staining was conducted to measureLC densityand Treg infiltration.Moreover,Western blot analysiswas performed to detect PI3K and MAPK signalingcascades.Flow cytometry wasused to determine thesurfaceactivation markers on LCs,Tcell subgroups,and apoptosis.ResultsThe antigenpresentation abilityand LCs density in the CT/HPV coinfection group were lower than those in the HPV and CT infection groups ( P <0.05),and those in the HPV infection group were lower than those in the control group( P <0.05).The PI3K signaling cascade was further activated,whereas the MAPK pathways were reduced in the CT/HPV coinfection group compared with the HPV and CT infection groups,leading to deeper immune suppresion in the CT/HPV coinfection group.There was less CD4+T cell and more Tregcell infiltration in the CT/HPV coinfection group than in the HPV and CT infection groups ( P <0.05). CD8*T cells became fewer in the CT/HPV group without significance,the CD4+/CD8*ratio was decreased and lymphocyte apoptosis was increased in the CT/HPV coinfection group compared to the HPV infection group. ConclusionCT infection can inhibit LCs function byreducing LCsantigen-presenting ability,affcting PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways, reducing CD4+and CD8*T cels,and increasing apoptosis, thus deepening immunosuppression caused by HPV infection,leading to continuous HPV infectionand acelerating the process cervical cancer.
【 words】Chlamydia trachomatis;Human papilomavirus;Langerhans cell; Signaling;Pathway; Im-mune evasion
宫颈癌是女性常见恶性肿瘤,据《2020全球癌症统计报告》,2020年全球女性宫颈癌新发病例604127例,死亡病例341831例,位于女性恶性肿瘤的第四位[1。(剩余12787字)