安塞地区长9储层成岩作用及孔隙演化规律

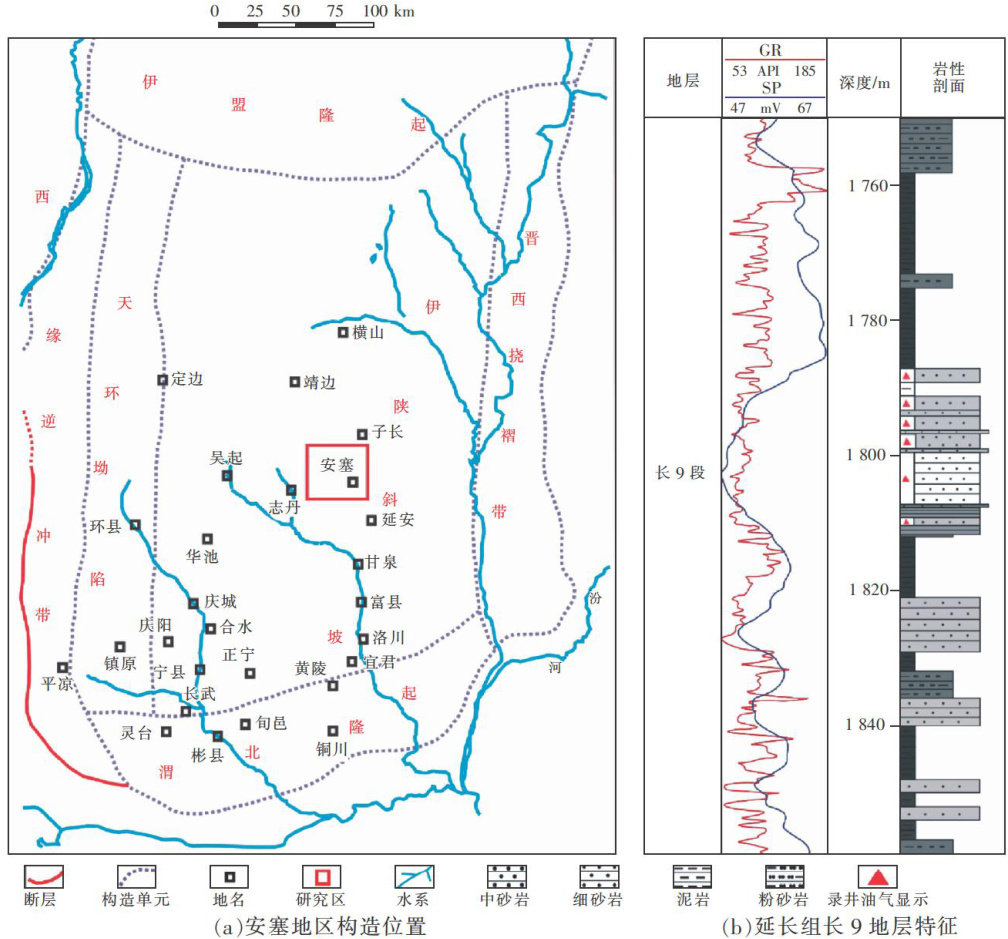
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P618.13 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1672-9315(2025)04-0784-11
DOI:10. 13800/j. cnki. xakjdxxb. 2025. 0414
Diagenesis and porosity evolution law of Chang 9 reservoir in Ansai area
WEI Shaoni 1 , WANG Xixi1, LIU Zhijun², ZHANG Chen², MENG Yue 3 LI Yongfeng³,HU Guilin³, ZHANG Tianjie
(1.Collegeof GeologyandEnvironment,Xi’anUniversityofScienceand Technology,Xi'an71Oo54,China; 2.Research Instituteof Explorationand Development ofChangqing Oilfield, Xi'an71Oo18,China; 3.No.1 Oil ProductionPlant, Changqing Oilfield Company,PetroChina, Yan'an716ooo,China)
Abstract: To investigate the diagenetic characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs and their influence on porosity evolution,Chang 9 reservoir of the Yanchang Formation in Ansai area of the Ordos Basin was selected as the research subject.A combination of techniques was employed including casting thin section observation, pore image,particle size analysis and physical property measurements.Based on the dominant pore types,the reservoirs were categorized into two types: residual intergranular pore-dominated and dissolution pore-dominated.The diagenetic features and differential porosity evolution patterns of these two reservoir types were analyzed.The results indicate that: Early-stage mechanical compaction significantly reduces reservoir porosity,and subsequent cementation further exacerbates reservoir densification. In contrast, dissolution processes improve reservoir quality by creating secondary pores through the removal of unstable mineral components.Reservoirs dominated by residual intergranular pores typically exhibit higher initial porosity,but the pore-reducing efects of compaction and cementation are more pronounced. Conversely,reservoirs dominated by dissolution pores have lower initial porosity,but the enhancement in porosity through dissolution is more significant,leading to the development of secondary pores and beter overall reservoir performance. These reservoirs are therefore considered relatively high-quality.This study elucidates the diferential mechanisms of porosity evolution controlled by diagenesis in tight sandstone reservoirs and provides a geological basis for heterogeneity evaluation and selection of sweet sopts in tight sandstone reservoirs in Ansai area of the Ordos Basin.
Key Words: Yanchang Formation; diagenesis; porosity evolution; Ansai area; Ordos Basin
0 引言
致密砂岩储层分布广泛、油气资源潜力巨大,储集特性复杂,是当今油气勘探开发的热点之二[1-3]。(剩余15412字)