Ca2+及钙结合蛋白与植物耐盐性关系的研究进展

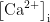
打开文本图片集
Research Progress on Relationship between Ca2+ and Calcium-Binding Proteins and Salt Tolerance in Plants
Li Cheng’,Du Chunyan²,Cui Xianfen³,Li Yancan',Li Jingjuan¹,Song Jie4,Cui Bing',Gao Jianwei(1. Vegetable Research Institute, Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Jinan 250100, China;2. Agriculture and Rural Bureau of Daiyue District, Taian City, Taian 271OOO,China;3. Tianzhuang Reservoir Comprehensive Service Center, Yiyuan County, Yiyuan 2561Oo, China ;4. College of Life Sciences, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 25oooo, China)
AbstractSoil salinization severely impacts crop productivity. As a pivotal secondary messenger in plant cells, Ca2+ plays a central role in mediating responses to salt stress. Calcium-binding proteins in plants perceive extracellular signals by binding Ca2+ . These proteins belong to an extensive gene superfamily including four subfamilies which were calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs)and their related kinases(CRKs), calmodulins (CaMs),calmodulin-like proteins(CMLs),and calcineurin B-like proteins(CBLs)paired with their interacting protein kinases ((CIPKs). Calcium-binding proteins play important roles in plants response to salt stress adaptation. This review synthesized current advances in understanding Ca2+ signaling and calciumbinding proteins in plant salt tolerance,and mainly discussed the regulatory effects of Ca2+ on salt-stressed crops and the function of calcium-binding proteins to crop salt resistance.Finally,the research and application prospects of calcium-binding proteins were prospected.
Keywords Ca2+ ; Calcium-binding protein; Salt stress; Salt tolerant mechanism
盐胁迫对植物生长有重大危害,显著影响作物产量。(剩余21021字)