甜瓜掌状裂叶p基因对贮藏期果实后熟生理的调控作用

打开文本图片集
Regulatory effect of the palmate-lobed leaf gene pll on the post-harvest physiology of melon fruits during storage
ZHANG Qiang1, YONG Liangmin1, DAI Wenting², SHI Yunjiao¹
(1.Hinanlsfse
al Sciences,Haikou 571100,China)
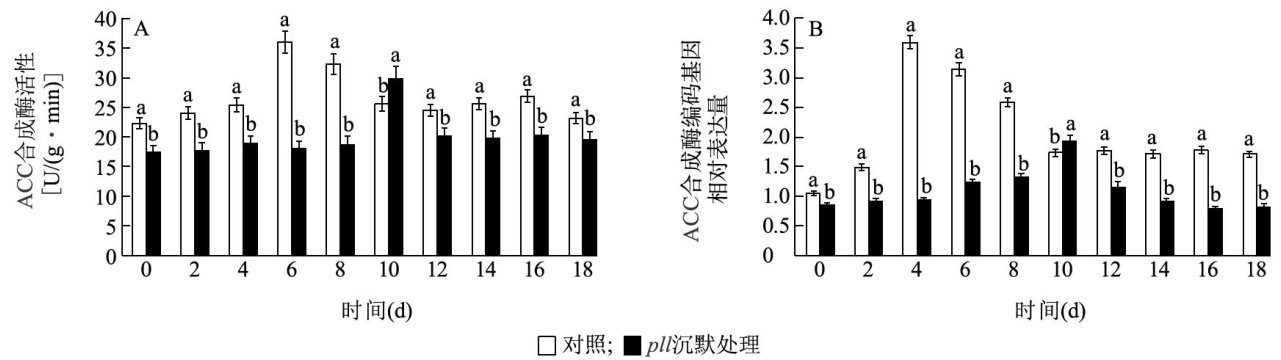
Abstract: The melon palmate-lobed leaf gene pll belongs to AINTEGUMENTA(ANT) transcription factor gene, which playsan importantrole inregulating plant growthand fruit development.During theresearch,the gene silencing of pll was detected byvirus-induced gene silencing(VIGS)technique.Thechanges of lipoxygenase activity,ethylene release and respiratory metabolism in fruits under normal and silent expression of pll gene were compared,and the effects of pl (204号 gene silencing inhibitiononthe expression of ethylene synthesisand sugar metabolism enzyme-encoding genes and related enzyme activities in fruitswere studied.The results showed that the low expression of pll gene in fruits could reduce the activityof lipoxygenase,ethylene release and respiration rate.Moreover,the pll gene had a positive regulation efect on ethylene synthesis and carbohydrate metabolism gene expression in fruits,and when the expression of pll gene was suppressed by silencing,the expresion of genes related to ethylene synthesisand glucose metabolism in fruits was also dow-regulated, thus reducing the activities of ethylene synthesis and glucose metabolism enzymes.It can be seen that the pll gene is in
收稿日期:2024-10-29
volvedintheregulationofpost-harvestphysiology,andthe down-regulation of pll gene expression has a delayed and inhibitory effect on the post-harvest physiological metabolismof melon fruits.
Key words:muskmelon; pll gene; gene silen-cing;enzymeactivity;post-harvest physiology
甜瓜(CucumismeloL.)主要产于中国西部地区,其农艺性状优良,果型匀称,口感与风味俱佳,深受消费者喜爱。(剩余11405字)