基于扫描光镊技术的多粒子力测量与流变学分析

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:O439文献标志码:A
Abstract: This study introduces a method for multiparticle force measurement and rheological analysis using a high-precision optical tweezers system, aiming to address the challenge of simultaneouscharacterization ofinteraction forcesand medium viscoelasticityatthe micro/nanoscale. Experiments utilizing the Aresis Tweez 30o scanning optical tweezers system achieved trapping and manipulation of 2.5-μm -diameter SiO2 particles, enabling high-resolution measurement of solvent-mediated interparticle forces (approximately 20fN )andinvestigationof cellulose solution rheology ( 1% mass concentration), including storage modulus and viscosity. The results demonstrated that the scanning optical tweezers system could accurately measure interparticle interaction forces and characterize the dynamic response of complex fluids. By combining multicycle averaging techniques and real-time tracking methods, the signal-to-noise ratio of the system was significantly enhanced, rendering it suitable for dynamic analysis at the micro/nanoscale. This research highlights the broad application potential of scanning optical tweezers technology in colloid science,biophysics,and materials science,providing a novel methodology for micro/nanoscale force and rheology studies.
Keywords: scanning optical tweezers technology; multi-particle manipulation; solvent-mediated force; microrheology; cellulose solution
引言
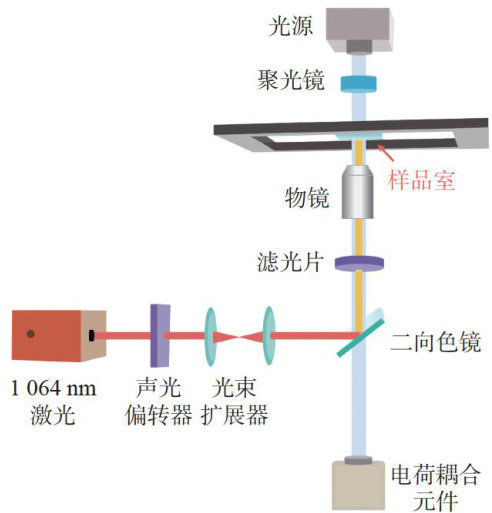
1实验系统与样品
光镊技术由 Ashkin等[1于1986年首次提出,已成为微纳米尺度下操控和测量微小粒子的重要工具。(剩余8320字)