不同应变率下皮质骨压缩力学实验与本构模型

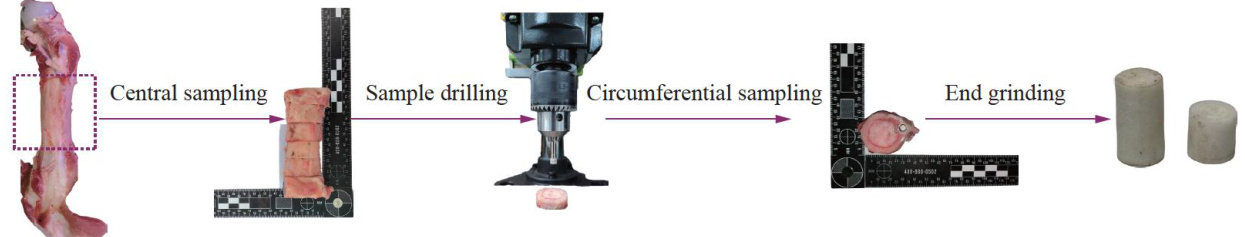
打开文本图片集
Study on compressive mechanical tests constitutive models cortical bone under different strain rates
Abstract:Corticalbone,asacriticalcomponent the human skeletalsystem,effectivelydispersesabsorbs external impactforces,protectingtheinternal medullrycavitysurroundingsttissues,organsfromdamage.Inorderto investigate the mechanicalresponsecortical boneunder impactloading,quasi-staticdynamiccompression experiments were conducted on porcinecortical bone at varying strain ratesusing a universal material testing machine a split Hopkinson pressure bar apparatus.The compression deformation characteristics corticalbone were observed by employing ultra-depththree-dimensional microscopydigital imagecorrelationtechnques.Aviscoelasticdmageconstitutivemodel wasapplied to fittheexperimentaldata,themodel parameters weredetermined.Theresultsdemonstratethat the compression process cortical boneischaracterized bythe initiationpropagation microcracksmechanical properties thematerialexhibitsignificantstrain-ratedependence.Theelastic modulus,yieldstress,compresivestrngth increase significantlywith increasingstrainrates.Underquasi-staticloading,thestress-straincurveconsists distinct elastic plasticdeformationstages.Incontrast,underhigh-strain-rate loading,thestress-strainresponseremainspurelyelasticat strains below 0.2% ,but transitions into a highly nonlinear regime with increasing compresson.Notably,no significant plastic deformation ocurs under dynamic loading,revealing pronounced viscoelastic behavior. Comparison between the experimental datatheoreticalcurves fromtheconstitutive modelshows goodagreement,withminimaldeviationsbetweenpredictednd measuredvalues.Themodelaccuratelycaptures thecompressivemechanical behaviorcorticalboneacrossdiferentstrain rates.Thisstudyprovides theoreticalreferences forthe treatment impact-inducedhuman injuries protective designs. Keywords:cortical bone; impulsive load; viscoelastic; strain rate;constitutive model
皮质骨作为人体骨骼的主要组成部分,占骨量的 80% ,分布于长骨两端以及短骨、扁骨和不规则骨的内部,凭借其卓越的抗压能力,能有效承载身体质量和抵御外部冲击[1-2]。(剩余13369字)